Genetic types and distinguished characteristics of dolomite and the origin of dolomite reservoirs
|
Genetic types and distinguished characteristics of dolomite and the origin of dolomite reservoirs |
| Wenzhi ZHAO,Anjiang SHEN,Zhanfeng QIAO,Liyin PAN,Anping HU,Jie ZHANG |
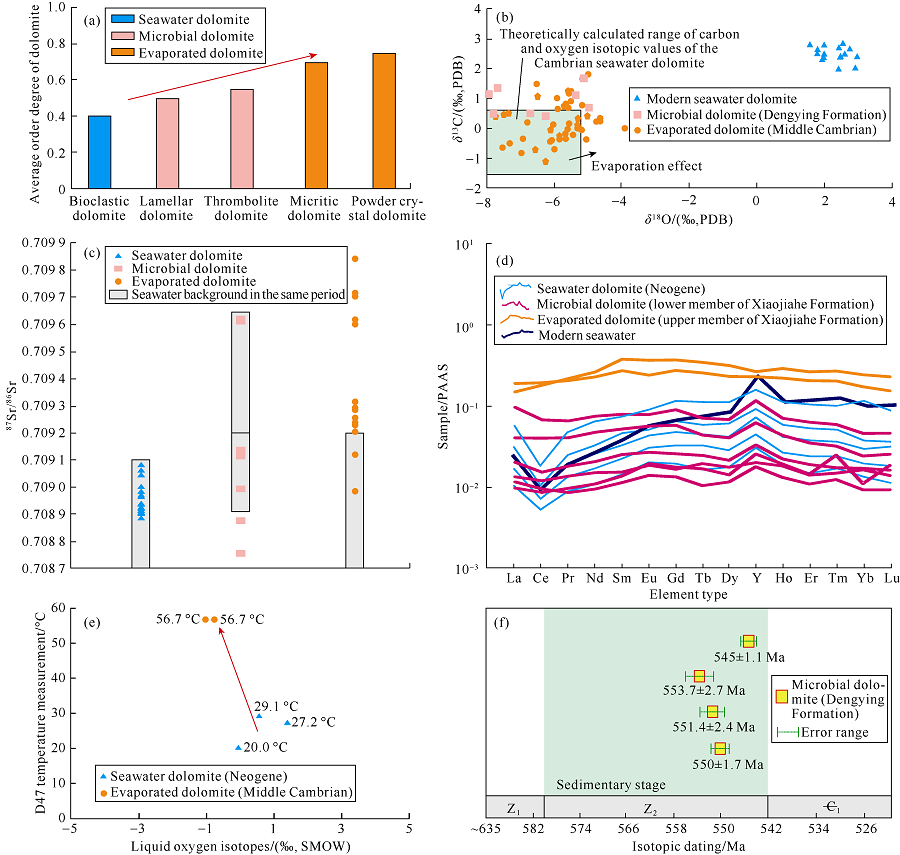
| Fig. 3. Geochemical characteristics and their variation trend of (pene-)contemporaneous low-temperature dolomite from (island) seawater dolomite, microbial dolomite to evaporated dolomite. (a) Order degree of dolomite is generally low, but shows an increasing trend; (b) Carbon and oxygen isotopic values shift from low positive to low negative gradually; (c) Sr isotope ratio turns from equivalent to that of contemporary seawater to higher than that of contemporary seawater gradually; (d) Values of the rare-earth elements turns from equivalent to higher than the reference value of contemporary seawater; (e) The ancient temperature measured by oxygen isotope (D47) turns from normal to higher gradually; (f) The isotopic age is equivalent to or younger than the formation age. |

|