Mixed carbonate rocks lithofacies features and reservoirs controlling mechanisms in a saline lacustrine basin in Yingxi area, Qaidam Basin, NW China
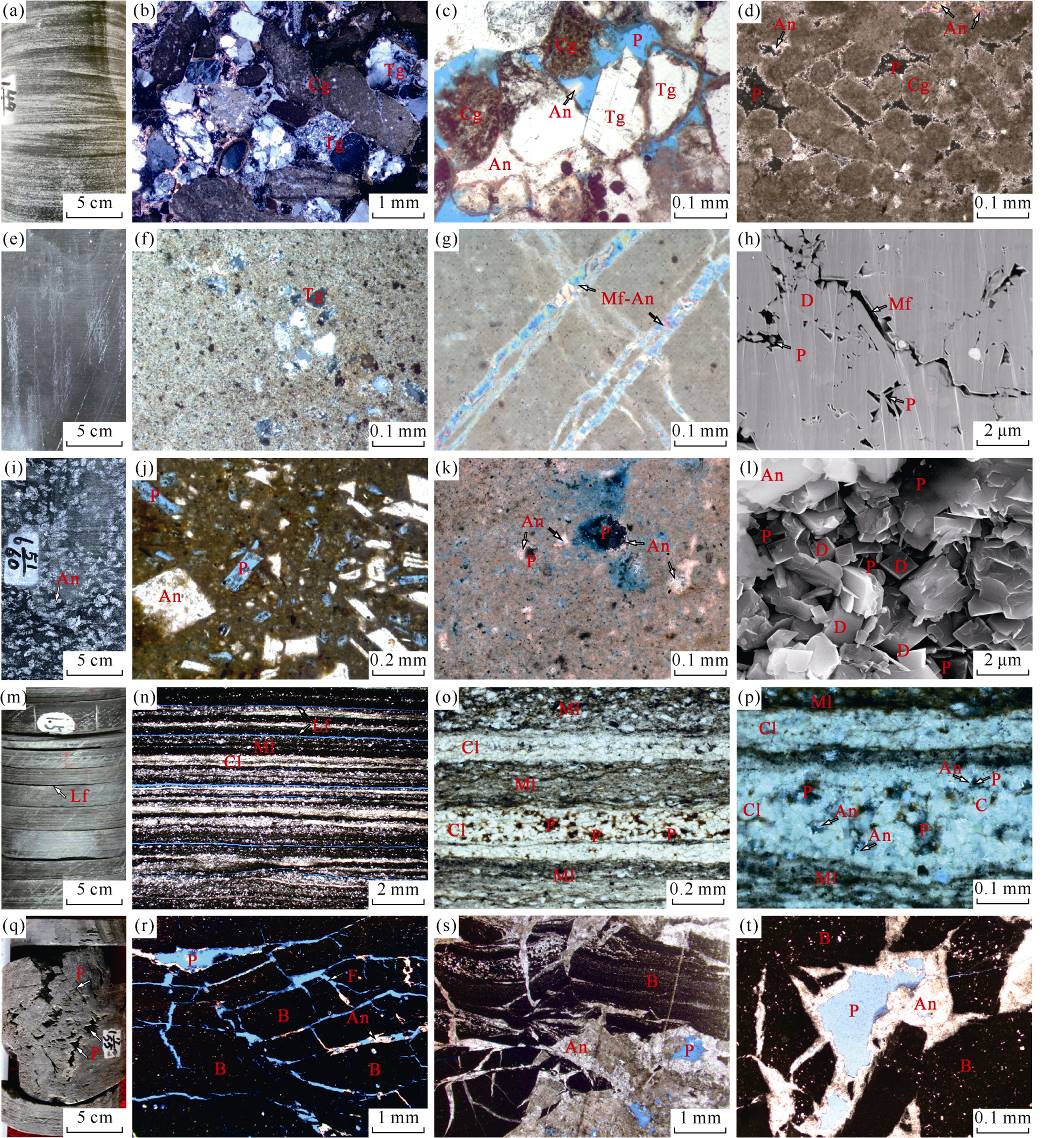
Mixed granular facies (a-d): (a) Well S41-2, 4126.20-4126.40 m, core, with cross bedding; (b) Well S49-1, 3862.15 m, cast thin section, cross-polarized light, terrigenous grains are developed, mostly oolitic, forming a mixed particle structure with carbonate grains; (c) Well S41-6-1, 3868.57 m, blue cast thin section, plane-polarized light, the particle composition and structure are the same as those shown in (b), the inter- granular dissolved pores are developed, and the anhydrite cement has the characteristics of dissolution residuals; (d) Well S43, 3922.77 m, cast thin sections, cross-polarized light, the particle composition is mainly carbonate grains with inter-granular dissolved pores, and the anhydrite cement is characterized by dissolution residuals. Massive calcareous dolostone facies (e-h): (e) Well S41-6-1, 3867.47-3867.67 m, core, homogeneous massive hybrid structure, without bedding; (f) Well S41-6-1, 3854.87 m, cast thin sections, cross-polarized light, carbonate, terrigenous clay and silty clastic grains are mixed to form a massive micrite structure; (g) Well Shi 41-2, 4178.16 m, cast thin section, cross-polarized light, two-stage microfracture filled with anhydrite; (h) Well S32X, 4125.99 m, backscattered scanning electron microscope, with microfractures and nano-scale dolomite intercrystalline pores developed. Plaque gypsum-bearing to gypso calcareous dolostone facies (i-l): (i) Well S41-2, 4126.5-4126.70 m, core, plaque distribution of evaporite minerals such as anhydrite; (j) Well S38-4, 3731.10 m, blue cast thin sections, plane-polarized light, stripped anhydrite crystals dissolved to form crystal molded pore; (k) Well S41-6-1, 3866.58 m, blue cast thin section, cross-polarized light, dissolved micro-pores developed, and microcrystalline-porphyritic anhydrite showed dissolved residual characteristics; (l) Well S41-2, 4178.16 m, scanning electron microscope, dolomite intercrystalline pores are developed. Laminated dolomitic limestone facies (m-p): (m) Well S41-6-1, 3850.80-3851.00 m, core, shale-like characteristics, with laminar fractures; (n) Well S41-6-1, 3854.80 m, blue cast thin section, plane-polarized light, argillaceous debris laminae and calcite laminae form high-frequency rhythms, and laminar fractures developed; (o) Well S41-6-1, 3865.80 m, thin section of rock without oil washing, plane-polarized, pores developed in the calcite lamina and full of oil; (p) Well S41-6-1, 3865.80 m, thin section of rock without oil washing, cross-polarized photograph, partial magnification of D3, anhydrite cement with dissolution residues on the edges of oil-saturated pores, which are mainly solved pores for anhydrite cement. Tectonic breccia calcareous dolostone facies (q-t): (q) Well S40, 3147.61-3147.81 m, core, massive calcareous dolostone crumpled and brecciated, large-scale fractures and vugs developed, and the mudstone strata at the bottom and top are flat, with only plastic deformation; (r) Well S40, 3150.66 m, blue cast thin section, plane-polarized light, with well-developed network microfractures and pores between tectonic breccia; (s) Well S32X, 4125.59 m, blue cast thin section, single-polarized light, brecciated fractures and vugs severely filled by late anhydrite, and a few inter-gravel pores remained; (t) Well S3-1, 4374.69 m, blue cast thin section, single-polarized light, anhydrite weakly filled the pore space between tectonic breccia, with well-developed vugs. Tg—terrigenous grain; Cg—carbonate grain; An—anhydrite; P—pores; Mf—microfracture; D—dolomite; Lf—laminar fractures; Cl—carbonate lamina; Ml—muddy lamina; F—fracture; B—tectonic breccia.