The dating and temperature measurement technologies for carbonate minerals and their application in hydrocarbon accumulation research in the paleo-uplift in central Sichuan Basin, SW China
|
The dating and temperature measurement technologies for carbonate minerals and their application in hydrocarbon accumulation research in the paleo-uplift in central Sichuan Basin, SW China |
| SHEN Anjiang,ZHAO Wenzhi,HU Anping,WANG Hui,LIANG Feng,WANG Yongsheng |
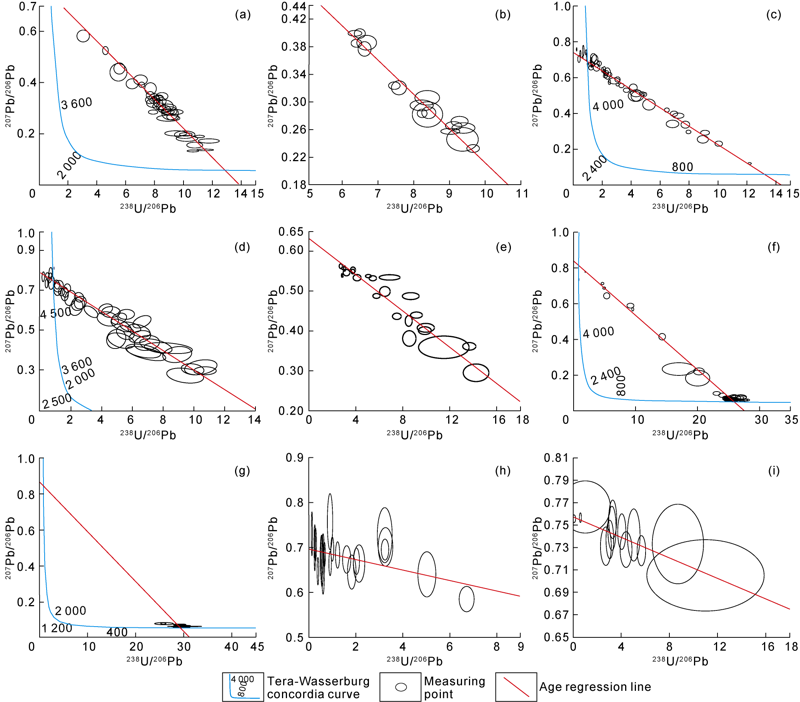
| Fig. 4. Laser in-situ U-Pb isotopic ages of dolomite minerals. (a) Ebian Xianfeng section, Deng 2 Member; the U-Pb isotopic age of fine-medium crystalline dolomite is (482±14) Ma; (b) Well Moxi 22, Deng 2 Member, 5416.90 m; the U-Pb isotopic age of fine-medium crystalline dolomite is (472±21) Ma; (c) Well Moxi 22, Deng 2 Member, 5418.70 m; the U-Pb isotopic age of fine-medium crystalline dolomite is (468±12) Ma; (d) Well Gaoshi 6, Deng 2 Member, 5363.04 m; the U-Pb isotopic age of fine-medium crystalline dolomite is (416±23) Ma; (e) Gucheng section, Deng 2 Member; the U-Pb isotopic age of coarse crystalline dolomite is (248±27) Ma; (f) Gucheng section, Deng 2 Member; the U-Pb isotopic age of coarse crystalline dolomite is (246.3±1.5) Ma; (g) Yangba section, Deng 2 Member; the U-Pb isotopic age of coarse crystalline dolomite is (216.4±7.7) Ma; (h) Gucheng section, Deng 2 Member; the U-Pb isotopic age of saddle-shaped dolomite is (115±69) Ma; (i) Well Gaoshi 1, Deng 4 Member, 4985.00 m; the U-Pb isotopic age of saddle-shaped dolomite is (41±10) Ma. |

|