Classification and control factors of pore-throat systems in hybrid sedimentary rocks of Jimusar Sag, Junggar Basin, NW China
|
Classification and control factors of pore-throat systems in hybrid sedimentary rocks of Jimusar Sag, Junggar Basin, NW China |
| XIAO Dianshi,GAO Yang,PENG Shouchang,WANG Meng,WANG Min,LU Shuangfang |
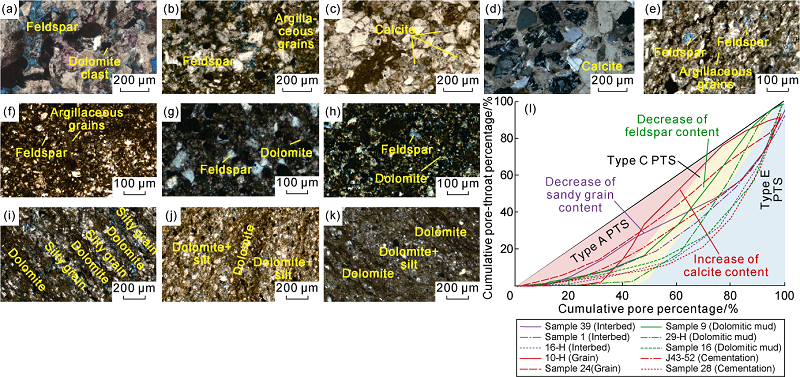
| Fig. 8. Thin section images and pore-throat system distribution of samples with different matrix support modes. (a) Sample 10-H, grain support mode, lime-bearing siltstone, with a calcite content of 9.8%; (b) Sample 24, grain support mode, argillaceous siltstone, with a calcite content of 10.1%; (c) Sample J43-52, partially cementation support mode, lime-bearing siltstone, with a calcite content of 13.9%; (d) Sample 28, cementation support mode, calcareous siltstone, with a calcite content of 36.3%; (e) Sample 9, mud grain support mode, silty mudstone, with a feldspar content of 52.5%; (f) Sample 16, mud grain support, dolomite-bearing mudstone, with a feldspar content of 25.1%; (g) Sample 29-H, dolomite support, dolomitic siltstone, with a feldspar content of 50.2%; (h) Sample 11, dolomite support, argillaceous dolomite, with a feldspar content of 16.3%; (i) Sample 39, interbed support mode, interbedding of silty dolomite, silt grains, and dolomicrite; (j) Sample 1, silty dolomite, interbedding of dolomicrite and dolomite-silt mixed layer; (k) Sample 16-H, silt-bearing dolomite, interbeds of dolomite and dolomite-silt; (l) Pore-throat system distribution characteristics of these samples. |

|