Differential structure of Ordovician karst zone and hydrocarbon enrichment in paleogeomorphic units in Tahe area, Tarim Basin, NW China
|
Differential structure of Ordovician karst zone and hydrocarbon enrichment in paleogeomorphic units in Tahe area, Tarim Basin, NW China |
| ZHANG San,JIN Qiang,HU Mingyi,HAN Qichao,SUN Jianfang,CHENG Fuqi,ZHANG Xudong |
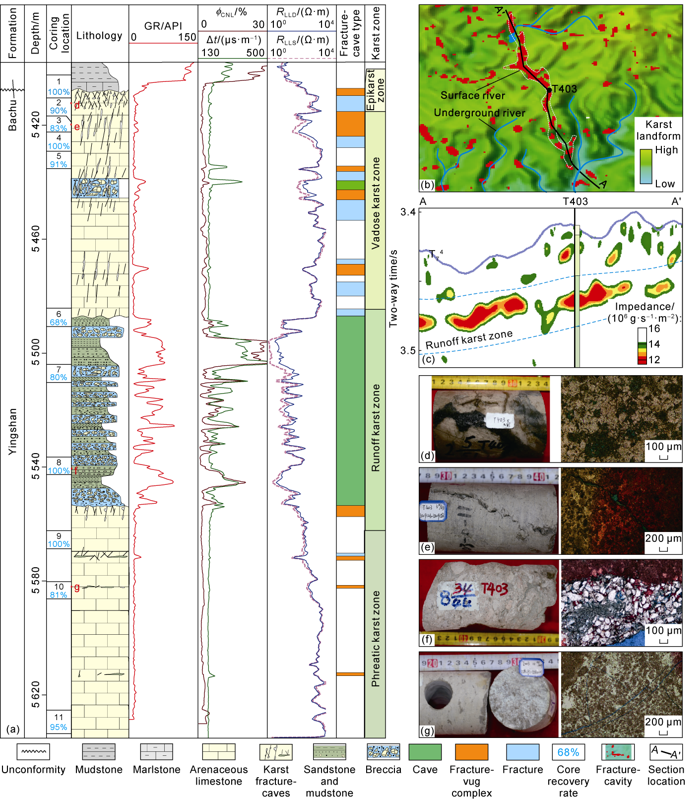
| Fig. 2. Types of Ordovician karst zones and characteristics of fracture-caves in Tahe area. (a) Comprehensive interpretation histogram of Well T403; (b) Hydrogeomorphology and distribution of fractures and caves in T403 well area during karst period; (c) The impedance profile of the underground river across well T403; (d) Well T403, 5412.03 m, brown-gray arenaceous limestone with crude oil filling karst fractures, and densely developed karst vuggies (blue in thin slice); (e) Well T403, 5419.58 m, brown-gray arenaceous limestone, developed fracture-cave complexes, and expanded along the fractures (blue in thin slice); (f) Well T403, 5540.03 m, conglomerate filled in the cave, and the gravel composition is arenaceous limestone, which is poorly sorted and well rounding, quartz particles are filled between the gravels, with intergranular pores (blue in slice); (g) Well T403, 5582.01 m, brown-gray arenaceous limestone developed bedding corrosion fissures with filled with gray-green mud, meanwhile development open fractures, joints which flat surface, and there is almost no evidence of corrosion expansion. |

|