Introduction
1. Tubular string structure, special tools and technical principle
1.1. Structure design and operation principle
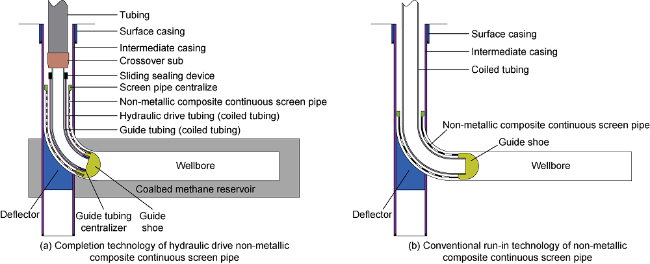
Fig. 1. Schematic diagram of completion tubular string structure for ultra-short radius horizontal wells. |
1.2. Key devices
1.2.1. Guide shoe
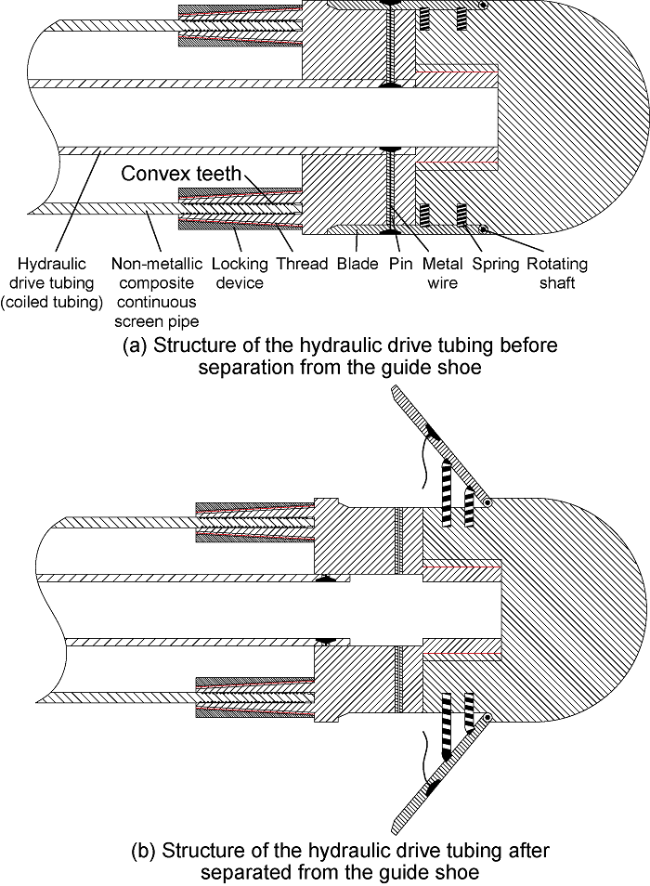
Fig. 2. Schematic diagram of guide shoe structure. |
1.2.2. Guide tubing centralizer and sliding sealing device
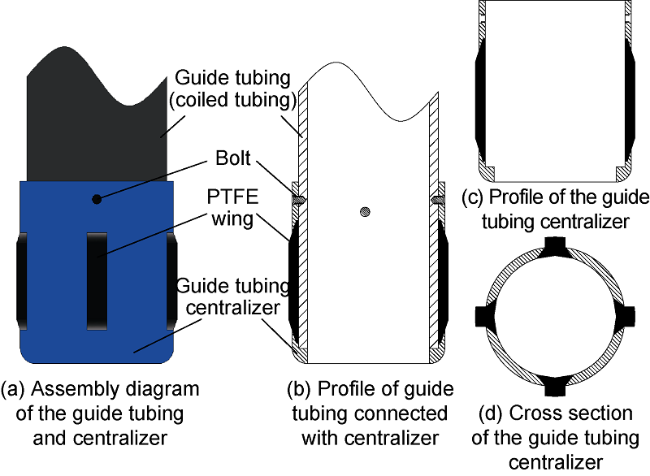
Fig. 3. Schematic diagram of the guide tubing centralizer. |
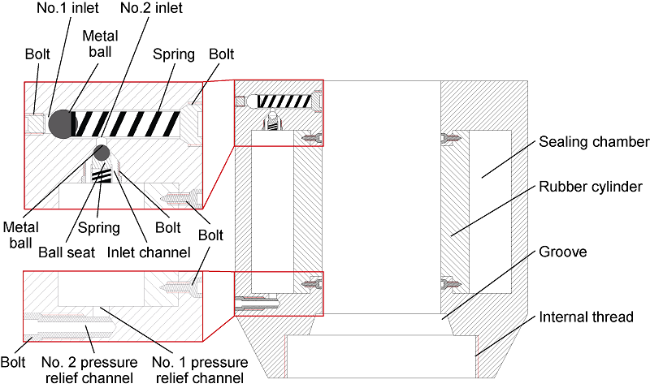
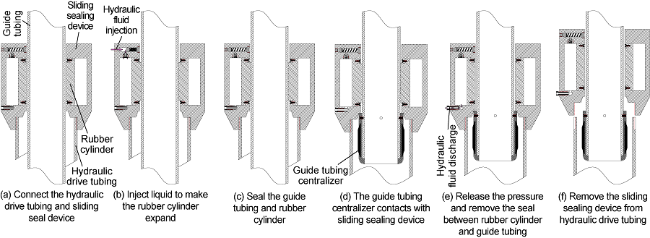
Fig. 4. Structure diagram of sliding sealing device. |
Fig. 5. Working principal diagram of the sliding sealing device. |
1.2.3. The crossover sub and non-metallic composite continuous screen pipe
Fig. 6. Schematic diagram of the crossover sub. |
Fig. 7. Photos of non-metallic composite continuous pipe. |
1.3. Completion process of hydraulic drive non-metallic composite continuous screen pipe
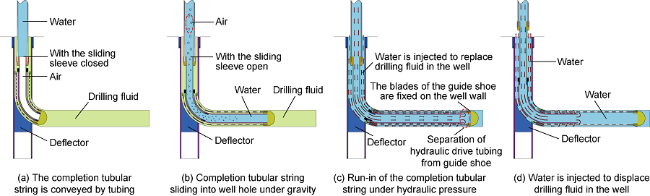
Fig. 8. Flow chart of hydraulic drive non-metallic composite continuous screen pipe running into ultra-short radius horizontal well. |
2. Mechanical-hydraulic coupling model
2.1. Tubular string mechanical model
2.1.1. Axial force and side force on the tubular string
2.1.2. The forces on sliding sealing device and guide shoe
2.2. Hydraulic drive model
2.2.1. Hydraulic load on completion tubular string
2.2.2. Pressure loss of the tubular string
2.3. Constraint conditions
3. Calculation and analysis of engineering case
3.1. Structural design of completion tubular string in ultra-short radius horizontal well
Table 1. Combination schemes of hydraulic drive tubing and guide tubing |
| No. | Completion string structure | Steel grade | Material | Yield strength/ kPa | Elastic modulus/kPa | Density/ (kg·m-3) | Outer Diameter/ mm | Inner Diameter/ mm | Minimum elastic bending radius/m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1# | Guide tubing | CT-90 | A-606Type4MOD | 620 528.2 | 206 842 719.8 | 7849 | 19.05 | 14.05 | 4.8 |
| Hydraulic drive tubing | CT-100 | A-606Type4MOD | 689 475.7 | 206 842 719.8 | 7849 | 31.75 | 27.69 | ||
| 2# | Guide tubing | CT-90 | A-606Type4MOD | 620 528.2 | 206 842 719.8 | 7849 | 12.70 | 7.70 | 3.8 |
| Hydraulic drive tubing | CT-100 | A-606Type4MOD | 689 475.7 | 206 842 719.8 | 7849 | 25.40 | 21.34 | ||
| 3# | Guide tubing | CT-90 | A-606Type4MOD | 620 528.2 | 206 842 719.8 | 7849 | 12.70 | 7.70 | 3.2 |
| Hydraulic drive tubing | CT-100 | A-606Type4MOD | 689 475.7 | 206 842 719.8 | 7849 | 19.05 | 14.05 |
3.2. Numerical calculation
3.2.1. Extending length of non-metallic composite screen pipe by conventional technology
Table 2. Orthogonal designs of the controlling factors of non-metallic composite screen pipe extending length for conventional technology |
| Level | Factor | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Coiled tubing size/mm | Curvature radius of wellbore/m | Friction coefficient | |
| 1 | 19.05 | 3.2 | 0.2 |
| 2 | 25.40 | 3.8 | 0.3 |
| 3 | 31.75 | 4.8 | 0.4 |
Table 3. Numerical calculation results of non-metallic composite screen pipe extending length with conventional technology |
| No. | Size of coiled tubing/mm | Curvature radius of wellbore/m | Friction coefficient | Extending limit/m |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 19.05 | 3.20 | 0.20 | 25 |
| 2 | 19.05 | 3.80 | 0.30 | 15 |
| 3 | 19.05 | 4.80 | 0.40 | 11 |
| 4 | 25.40 | 3.20 | 0.30 | 18 |
| 5 | 25.40 | 3.80 | 0.40 | 12 |
| 6 | 25.40 | 4.80 | 0.20 | 32 |
| 7 | 31.75 | 3.20 | 0.40 | 13 |
| 8 | 31.75 | 3.80 | 0.20 | 36 |
| 9 | 31.75 | 4.80 | 0.30 | 21 |
Table 4. Range analysis of numerical calculation results of non-metallic composite screen pipe extending length for conventional technology |
| Factor | K1/m | K2/m | K3/m | k1/m | k2/m | k3/m | r/m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coiled tubing size | 51 | 62 | 70 | 17.00 | 20.67 | 23.33 | 6.33 |
| Wellbore curvature radius | 56 | 63 | 64 | 18.67 | 21.00 | 21.33 | 2.67 |
| Friction coefficient | 93 | 54 | 36 | 31.00 | 18.00 | 12.00 | 19.00 |
Note: K1, K2 and K3 are the sum of extending limits of a certain factor at levels 1, 2 and 3. Taking the Level 1 (19.05 mm) of the coiled tubing size as an example, K1 = 25 + 15 + 11 = 51 m. k1, k2, k3 are the average value of extending lengths of a certain factor at levels 1, 2 and 3, respectively. Taking the Level 1 (19.05 mm) of the coiled tubing size as an example, k1=K1/3=17 m. r is the range, r=max (k1, k2, k3)-min (k1, k2, k3). |
Table 5. Variance analysis of numerical calculation results of non-metallic composite screen pipe extending length for conventional technology |
| Source | Sums of squared deviations | Degree of freedom | Mean square | Value of significant difference level | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coiled tubing size | 60.67 | 2 | 30.33 | 7.00 | Not significant |
| Wellbore curvature radius | 12.67 | 2 | 6.33 | 1.46 | Not significant |
| Friction coefficient | 566.00 | 2 | 283.00 | 65.31 | Significant |
| Error | 8.67 | 2 | 4.33 | ||
| Total | 648.01 | 8 | 323.99 |
3.2.2. The extending length of hydraulic drive non-metallic composite continuous screen pipe
Table 6. Orthogonal designs of the controlling factors of hydraulic drive non-metallic composite screen pipe extending length |
| Level | Factor | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Completion tubular string structure | Injection flow rate/(L·min-1) | Friction coefficient | |
| 1 | 1# | 1 | 0.2 |
| 2 | 2# | 3 | 0.3 |
| 3 | 3# | 6 | 0.4 |
Table 7. Calculation results of extending length of hydraulic drive non-metallic composite screen pipe |
| No. | Structure of completion tubular string | Injection flow rate/(L·min-1) | Friction coefficient | Extending limit/m |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1# | 1 | 0.2 | 655 |
| 2 | 1# | 3 | 0.3 | 510 |
| 3 | 1# | 6 | 0.4 | 379 |
| 4 | 2# | 1 | 0.3 | 301 |
| 5 | 2# | 3 | 0.4 | 228 |
| 6 | 2# | 6 | 0.2 | 381 |
| 7 | 3# | 1 | 0.4 | 250 |
| 8 | 3# | 3 | 0.2 | 427 |
| 9 | 3# | 6 | 0.3 | 333 |
Table 8. Range analysis of numerical calculation results of hydraulic drive non-metallic composite screen pipe extending length |
| Factor | K1/m | K2/m | K3/m | k1/m | k2/m | k3/m | r/m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Completion tubular string structure | 1 544 | 910 | 1 010 | 514.67 | 303.33 | 336.67 | 211.33 |
| Injection flow rate | 1 206 | 1 165 | 1 093 | 402.00 | 388.33 | 364.33 | 37.67 |
| Friction coefficient | 1 463 | 1 144 | 857 | 487.67 | 381.33 | 285.67 | 202.00 |
Table 9. Variance analysis of numerical calculation results of hydraulic drive non-metallic composite screen pipe extending length |
| Source | Sums of squared deviations | Degree of freedom | Mean square | Value of significant difference level | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Completion tubular string structure | 77 456.89 | 2 | 38 728.44 | 37.35 | Significant |
| Injection flow rate | 2181.56 | 2 | 1090.78 | 1.05 | Insignificant |
| Friction coefficient | 61 262.89 | 2 | 30 631.44 | 29.54 | Significant |
| Error | 2073.56 | 2 | 1036.78 | ||
| Total | 142 974.89 | 8 | 71 487.44 |
3.3. Applicability analysis of hydraulic drive completion tubular string
Table 10. Applicable conditions of hydraulic drive completion tubular string |
| Sidetracking casing size/ mm | Open hole size/ mm | Outer diameter of non-metallic composite continuous screen pipe/mm | Structure of completion tubular string | Outer diameter of hydraulic drive tubing/ mm | Outer diameter of guide tubing/mm | Wellbore curvature radius/m | Critical run-in velo- city of completion tubular string/ (m·min-1) | Injection flow rate/ (L·min-1) | Extending limit/m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 139.7 | ≥114 | ≥100 | 1# | 31.75 | 19.05 | ≥4.8 | 39.81 | 1.50-7.54 | 655 |
| 2# | 25.40 | 12.70 | ≥3.8 | 31.35 | 0.50-4.67 | 381 |
3.4. Mechanical and hydraulic analysis of completion tubular string
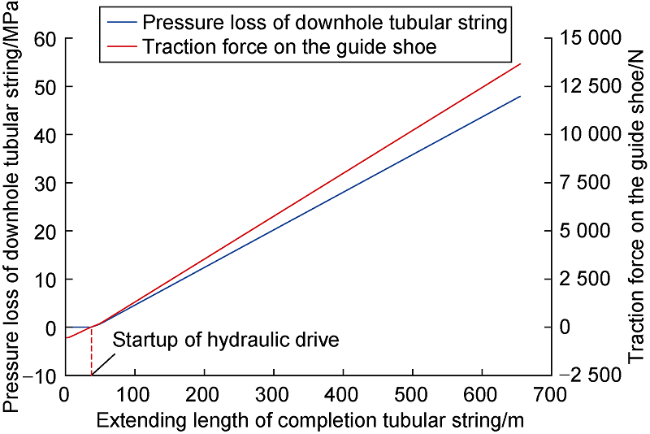
Fig. 9. Pressure loss of downhole string and traction force variation on the guide shoe with extending length. |
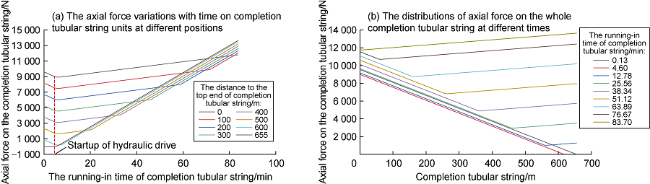
Fig. 10. Axial force curves of the completion tubular string. |