Introduction
1. Failure analysis and surface modification of sensor electrodes
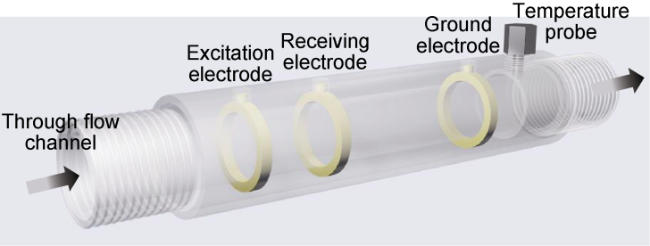
1.1. Sensor structure and working principle
Fig. 1. Structure schematic of the conductance water cut sensor. |
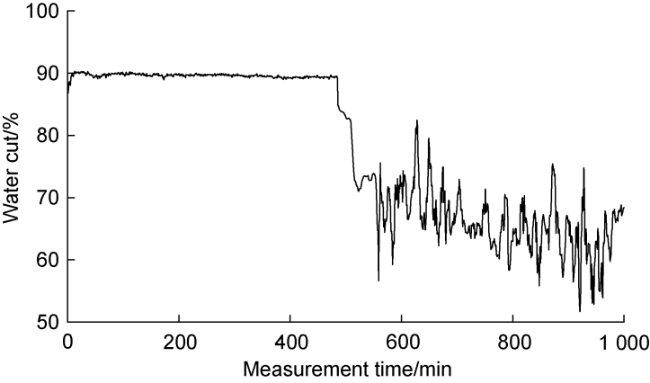
1.2. Failure mechanism
Fig. 2. Variation of measured water cut value over measurement time. |
1.3. Ways of electrode surface modification
2. BDD modified electrode preparation and tests
2.1. BDD film preparation
2.2. BDD film performance test
2.2.1. Test of erosion wear resistance
2.2.2. Test of electrochemical corrosion resistance
2.2.3. Test of oleophobic performance
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Test and analysis of erosion resistance performance
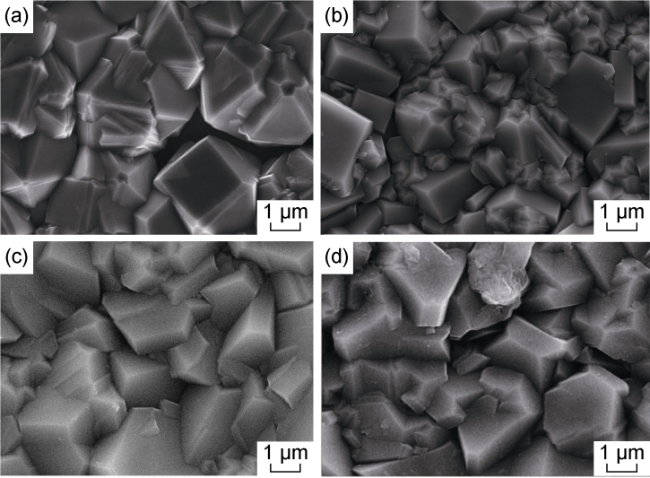
3.1.1. Microscopic morphology
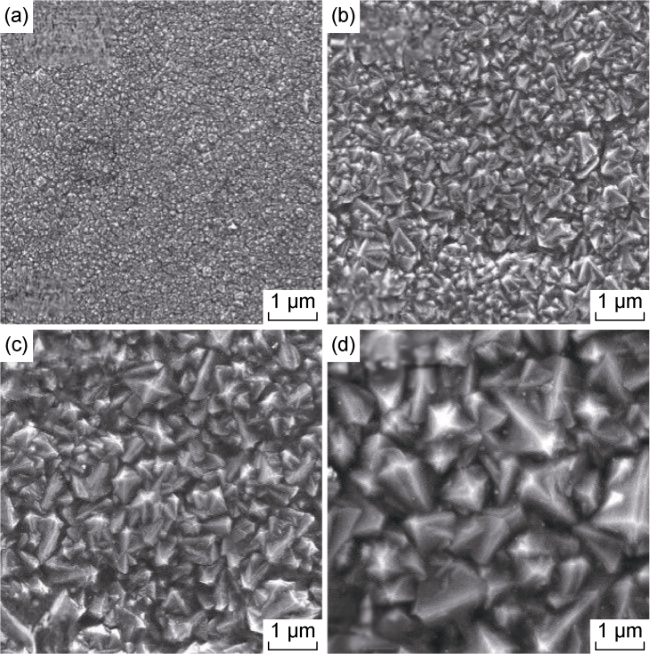
Fig. 3. SEM images of BDD films with four boron-doping concentrations. (a) A boron-doping concentration of 3×10-3; (b) A boron-doping concentration of 6×10-3; (c) A boron- doping concentration of 9×10-3; (d) A boron-doping concentration of 12×10-3. |
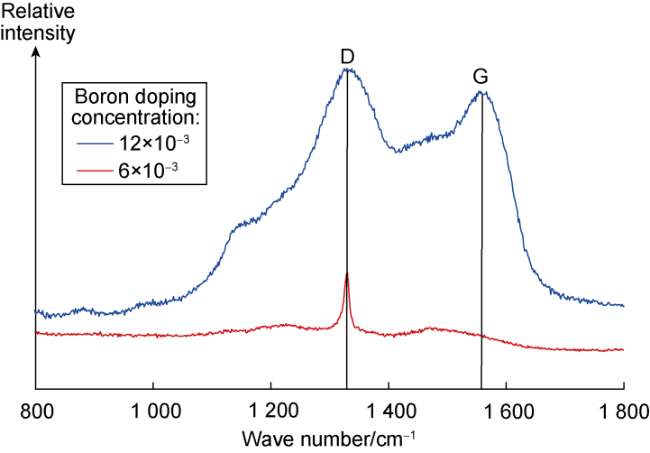
3.1.2. Carbon valence bond structure
Fig. 4. Raman spectra of BDD films prepared at two boron doping concentrations. |
3.1.3. Tribological performance
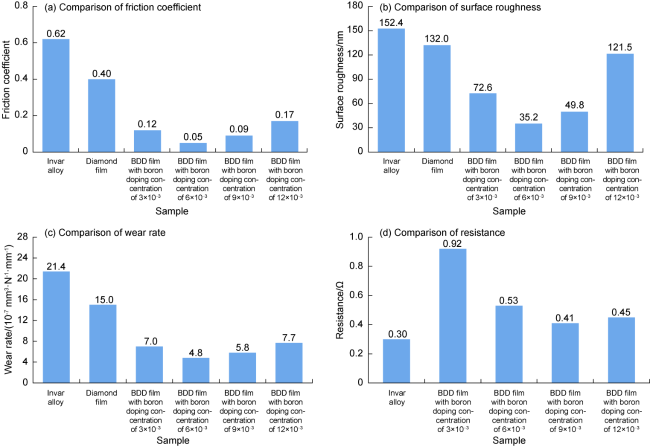
Fig. 5. Performances comparison of Invar alloy, boron undoped diamond film and four BDD films. |
3.1.4. Electrical conductivity
3.2. Test and analysis of electrochemical corrosion resistance
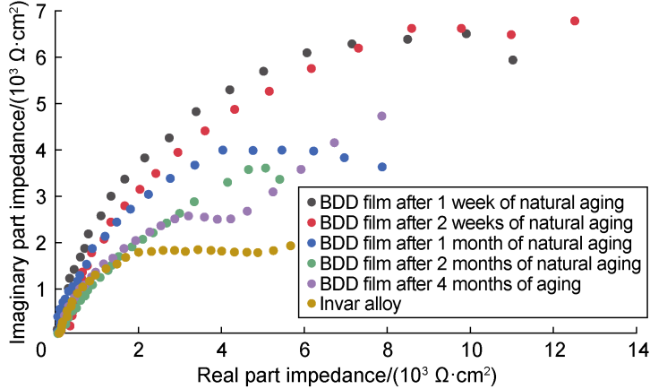
Fig. 6. Nyquist plots of Invar alloy and BDD films with five natural aging times. |
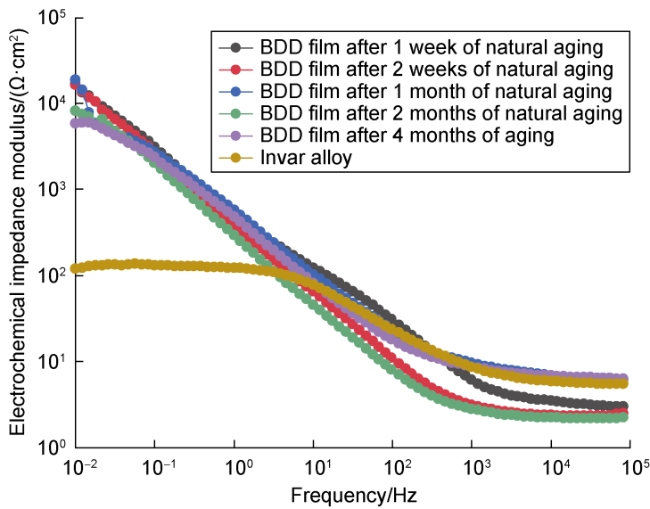
Fig. 7. Bode plots of Invar alloy and BDD films with five natural aging times. |
3.3. Test and analysis of oleophobic performance
Fig. 8. Morphologies of BDD films prepared with four deposition times. (a) 4 h of deposition; (b) 6 h of deposition; (c) 8 h of deposition; (d) 10 h of deposition. |
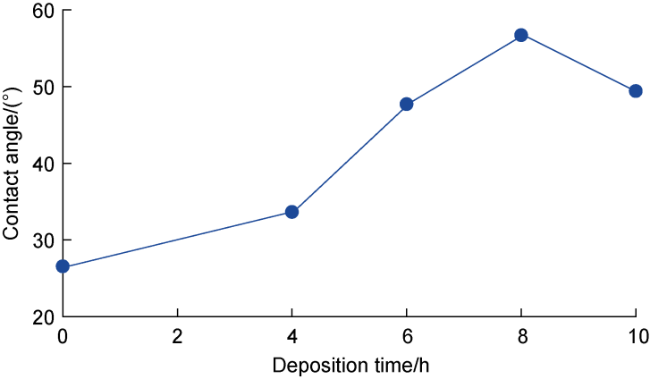
Fig. 9. Contact angles of Invar alloy (deposition time of zero) and BDD films with different deposition times. |
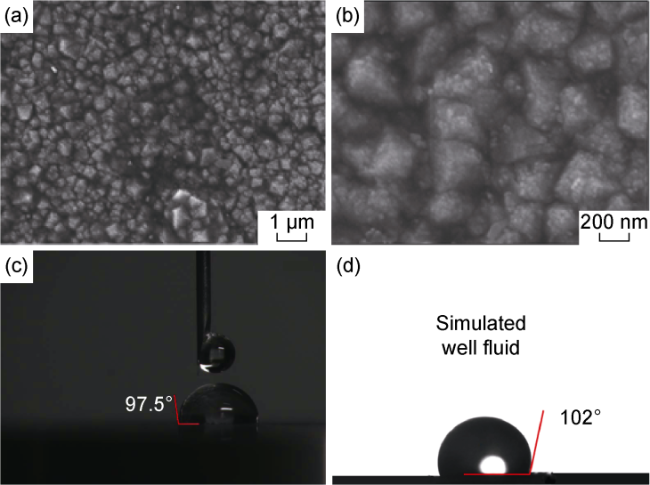
Fig. 10. Effect of fluorination treatment on wettability of BDD films. (a) SEM image at 5000 magnifications; (b) SEM image at 20 000 magnifications; (c) Contact angle of fluorinated samples; (d) Contact angle in simulated well fluid environment. |
4. Simulation of engineering test and sensor package
4.1. Erosion resistance
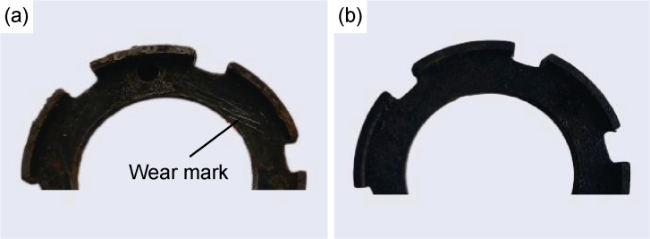
Fig. 11. Macroscopic erosion morphologies of electrode components (a) before and (b) after modification. |
4.2. Electrochemical corrosion resistance
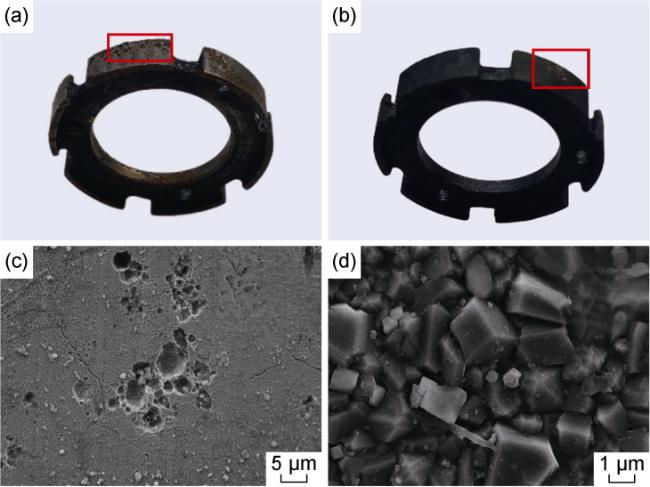
Fig. 12. Surface corrosion morphologies of electrode components. (a) Macroscopic corrosion morphology of uncoated electrode; (b) Macroscopic corrosion morphology of coated electrode; (c) Microscopic corrosion morphology of uncoated electrode; (d) Microscopic corrosion morphology of coated electrode. |
4.3. Oleophobic performance
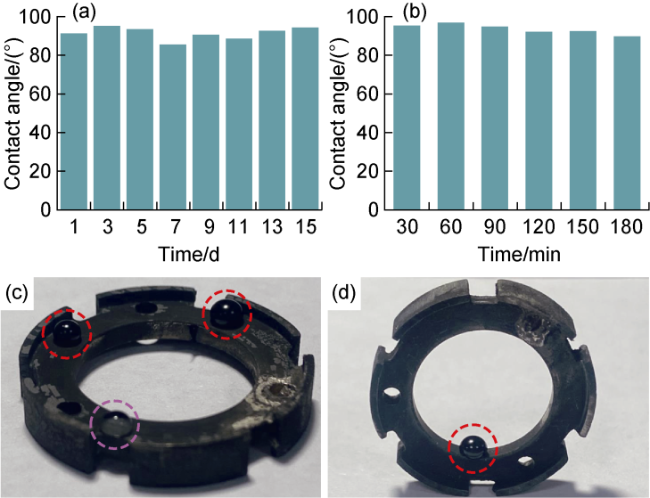
Fig. 13. Assessment of anti-oil adhesion stability of BDD film modified electrodes. (a) Oil contact angle in air; (b) Crude oil contact angle in well fluid; (c) Oil spreading on electrode surface, red circle shows the pattern of crude oil on treated electrode surface, and purple circle shows the pattern of two-phase mixture of crude oil and water on treated electrode surface; (d) Oil spreading on the inner wall of the electrode, red circle shows the pattern of crude oil on treated electrode surface. |
4.4. Sensor package
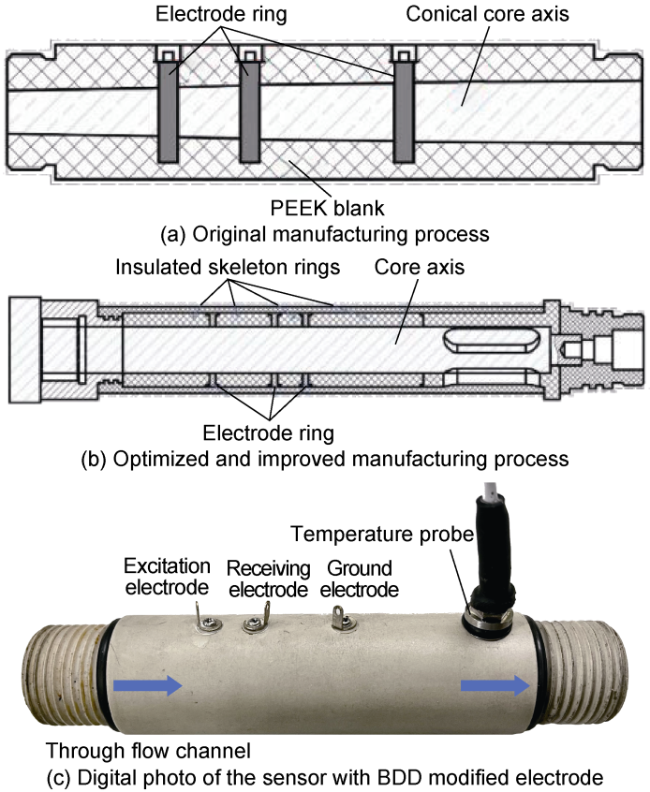
Fig. 14. Comparison of the packaging processes for water cut sensor and its digital photo. |