Introduction
1. Geological setting
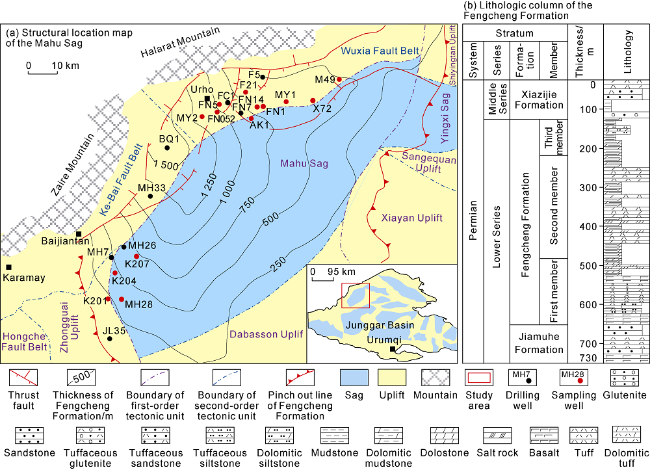
Fig. 1. Structural location map of the Mahu Sag (a) and lithologic column of the Fengcheng Formation (b). |
2. Samples and methods
3. Petrological characteristics of dolomitic rocks and microscopic characteristics of dolomites
3.1. Petrological characteristics of dolomitic rocks
3.2. Microscopic characteristics of authigenic dolomites
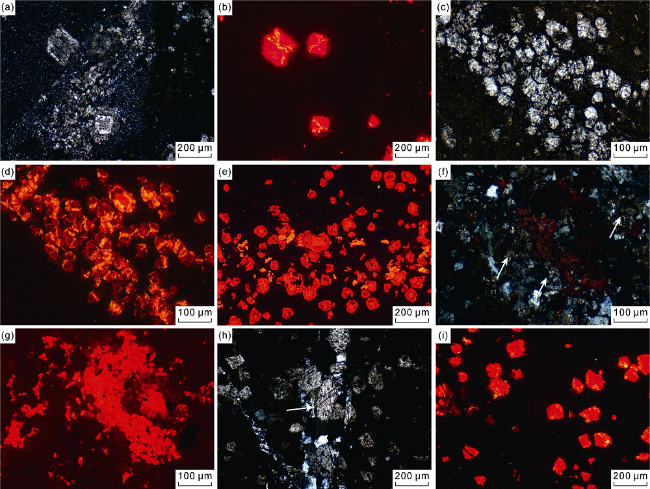
Fig. 2. Micro characteristics of the dolomites in dolomitic rocks of the Fengcheng Formation in the Mahu Sag. (a) Well FN14, 4162.77 m, P1f2, fine crystalline-silt-crystalline and subhedral-euhedral dolomites are distributed in tuffs in a floating form, under cross-polarized light; (b) Cathodoluminescence of the dolomites is orange red, with the same view field as (a), cathodoluminescence photomicrograph; (c) Well MY1, 4669.85 m, P1f2, silt-crystalline subhedral dolomites are distributed in a striped form, with order degree of 0.49, under plane-polarized light; (d) Cathodoluminescence of the dolomites with zonary structure is orange red-orange yellow, with the same view field as (c), cathodoluminescence photomicrograph; (e) Well MY1, 4595.34 m, P1f3, fine crystalline-silt-crystalline and subhedral dolomites are distributed in a striped form, with orange red cathodoluminescence and zonary structure, cathodoluminescence photomicrograph; (f) Well K204, 4348.05 m, P1f3, dolomites replace volcaniclastics (white arrow), with order degree of 0.71, under cross-polarized light; (g) Dolomites have non-cathodoluminescence, cathodoluminescence of calcites is orange red, with the same view field as (f), cathodoluminescence photomicrograph; (h) Well MY1, 4814.13 m, P1f2, fine crystalline and subhedral-euhedral dolomites (white arrow) filled in the fracture, with order degree of 0.97, under cross-polarized light; (i) Dolomites filling in the fracture have non-cathodoluminescence, in the same view field as (h), cathodoluminescence photomicrograph. |
4. Formation period of the dolomites
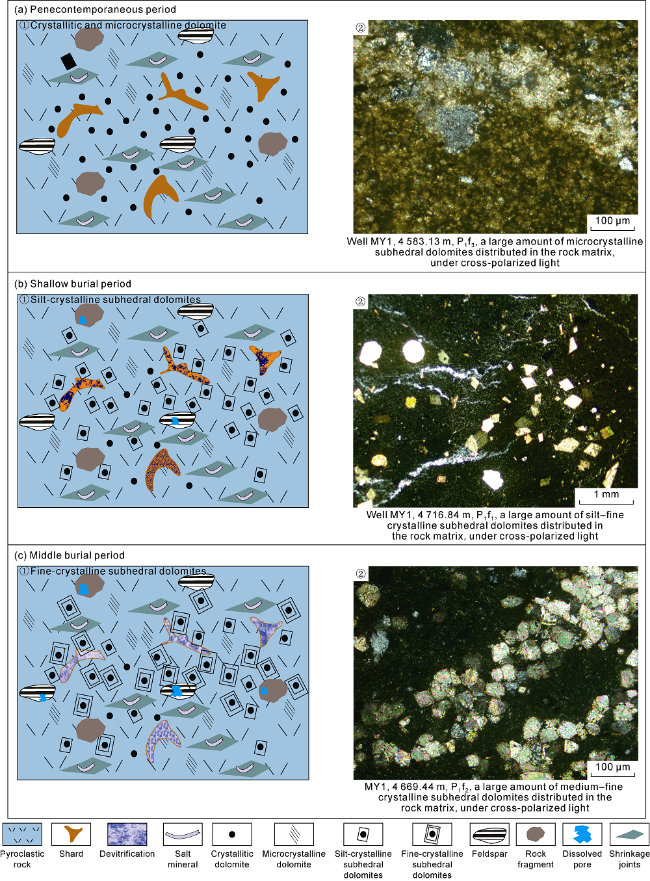
4.1. Identification of dolomite formation sequence based on microscopic occurrence characteristics
4.2. Temperature measurements of fluid inclusion and oxygen isotopic composition
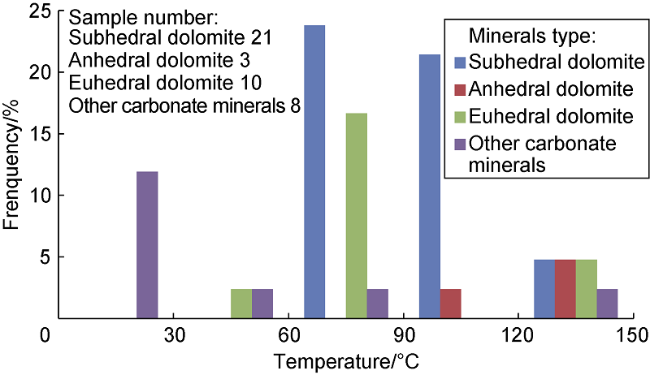
Fig. 3. Distribution of formation temperatures of dolomites and other carbonate minerals in the Fengcheng Formation of the Mahu Sag. |
4.3. Precipitation temperatures of dolomites deduced by microscopic fluorescence
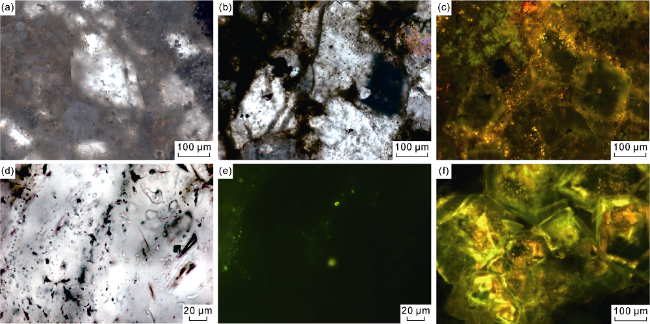
Fig. 4. Fluid inclusions and fluorescence characteristics of dolomites and their associated minerals in dolomitic rocks of the Fengcheng Formation in the Mahu Sag. (a) Well MY1, 4899.86 m, P1f1, salt water inclusions in the fine crystalline and subhedral dolomite, homogenization temperature of 68 °C, δ13C=2.07‰, δ18O=-0.86‰ (laser isotope measurement), under plane-polarized light; (b) Well FN14, 4165.90 m, P1f2, hydrocarbon inclusions in the subhedral dolomite, homogenization temperature of 91 °C, under plane-polarized light; (c) The subhedral dolomite inclusion with orange yellow fluorescence, in the same view field as (b), fluorescence photomicrograph; (d) Well K207, 4854.30 m, P1f2, hydrocarbon inclusions in the coarse-crystalline dolomite in the dissolved pore, homogenization temperature of 121 °C, δ13C=3.65‰, δ18O=2.29‰ (laser isotope measurement), under plane-polarized light; (e) The hydrocarbon inclusions in dolomite with green fluorescence, in the same view field as (d), fluorescence photomicrograph; (f) Well K204, 4333.05 m, P1f3, the subhedral dolomites with zonary fluorescence, fluorescence photomicrograph. |
4.4. Formation period deduced by order degrees of dolomites
5. Material sources and fluid evolution during dolomites precipitation
5.1. Material sources
5.1.1. Tracers of chemical compositions of rocks
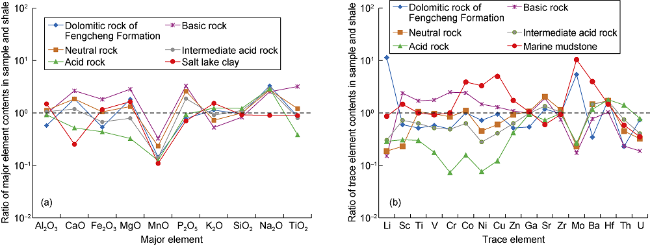
Fig. 5. Distribution pattern of major elements (a) and trace elements (b) in dolomitic rocks in the Fengcheng Formation of the Mahu Sag (data of igneous rocks (China) quoted from references [38-39]; data of average salt lake clay quoted from references [40-41]; data of shale and marine mudstone quoted from Reference [37]). |
5.1.2. Isotopic tracers
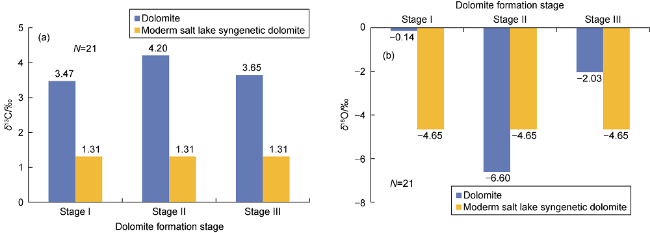
Fig. 6. Distribution histograms of average δ13C values (a) and average δ18O values (b) of the dolomites in dolomitic rocks of the Fengcheng Formation in the Mahu Sag (the δ13C and δ18O values of moderm salt lake syngenetic dolomite data from Reference [43], N represents sample number). |
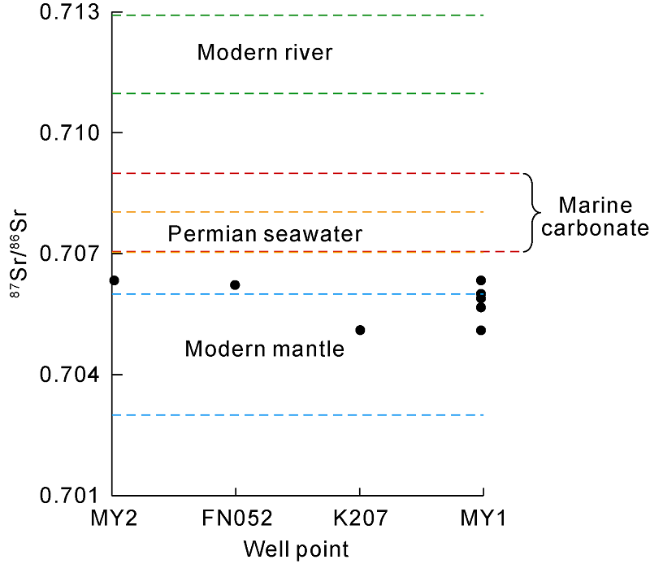
Fig. 7. Distribution of the 87Sr/86Sr values of dolomites in the dolomitic rocks of the Fengcheng Formation in the Mahu Sag and other strontium sources. |
5.1.3. Cathodoluminescence tracer of authigenic dolomites
5.2. Fluid evolution
Fig. 8. Electron microprobe sample point location and microscopic characteristics of dolomites from the Fengcheng Formation in the Mahu Sag. (a) MY1, 4610.86 m, P1f2, sample point location (white dot, number is sample point number) of electron microprobe of the dolomites with zonary cathodoluminescence, scanning electron micrograph image; (b) Dolomites with zonary cathodoluminescence, the same sample as (a), cathodoluminescence photomicrograph; (c) MY1, 4669.85 m, P1f2, sample point location of electron probe of striped dolomites, scanning electron micrograph image; (d) Dolomites with zonary cathodoluminescence, the same sample as (c), cathodoluminescence photomicrograph; (e) MY1, 4852.18 m, P1f1, sample point location of electron probe of metasomatic dolomites, backscattered electron image; (f) MY1, 4814.13 m, P1f1, dolomites filling in the fracture, scanning electron micrograph image. |
Table 1. Electron microprobe data of dolomites with different occurrences in the dolomitic rocks of the Fengcheng Formation of Well MY1 in the Mahu Sag |
| Depth/ m | Point number | Dolomite occurrence | Mass fraction/% | Fe/Mn | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MgO | SiO2 | MnO | SrO | Na2O | CaO | FeO | Al2O3 | K2O | ||||
| 4610.86 | 1 | Zonary form | 36.54 | 4.68 | 0.58 | 0.37 | 0.50 | 56.60 | 0.16 | 0.42 | 0.15 | 0.27 |
| 2 | 34.67 | 5.47 | 0.50 | 0.31 | 0.60 | 57.44 | 0.37 | 0.37 | 0.27 | 0.75 | ||
| 3 | 30.80 | 5.96 | 0.43 | 0.17 | 0.19 | 56.84 | 4.14 | 1.22 | 0.25 | 9.82 | ||
| 4 | 30.84 | 3.95 | 0.40 | 0 | 0.18 | 59.46 | 4.45 | 0.37 | 0.35 | 11.42 | ||
| 5 | 33.38 | 2.62 | 0.37 | 0.38 | 0.26 | 62.40 | 0.51 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 1.39 | ||
| 4669.85 | 1 | Striped form | 29.26 | 0.88 | 6.78 | 0.41 | 0.25 | 62.19 | 0.15 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.02 |
| 2 | 33.17 | 1.38 | 0.27 | 0.40 | 0.29 | 64.00 | 0.05 | 0.26 | 0.18 | 0.18 | ||
| 3 | 30.49 | 4.15 | 0.04 | 0.65 | 0.73 | 62.67 | 0.16 | 1.02 | 0.09 | 4.56 | ||
| 4852.18 | 1 | Metasomatic form | 22.95 | 20.19 | 0.49 | 0.00 | 0.28 | 43.98 | 1.63 | 5.71 | 4.77 | 3.36 |
| 2 | 33.92 | 4.16 | 0.40 | 0.51 | 0.78 | 59.77 | 0.08 | 0.15 | 0.23 | 0.20 | ||
| 3 | 32.52 | 5.31 | 0.52 | 0.47 | 0.94 | 59.41 | 0.28 | 0.23 | 0.32 | 0.54 | ||
| 4814.13 | 1 | Fracture-filling | 26.96 | 1.51 | 0.15 | 0.16 | 0.17 | 64.21 | 6.46 | 0.02 | 0.36 | 42.61 |
Note: The data in the table are normalized; sample point number locations are in |
6. Dolomite origin
Table 2. Characteristics of dolomites in different periods in the dolomitic rocks of the Fengcheng Formation in the Mahu Sag |
| Formation period | Sample temperature/°C | Crystal features | Main occurrence | Fluorescent color | Cathodoluminescence | Order degree | δ18O/ ‰ | Source of Mg2+ | Formation mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Penecontemporaneous- shallow burial | 55-89 | Euhedral, subhedral; microcrystalline, silt-crystalline | Striping, floating | Non-fluorescence, brown yellow | Orange red, orange yellow | 0.43- 0.66 | −4.53- 0.63 | Alkali lake saline water | Penecontemporaneous dolomitization induced by microorganism, seepage-reflux dolomitization |
| Middle burial | 91-118 | Subhedral; silt-crystalline, fine crystalline | Intergranular pore-filling, metasomatic | Orange yellow | Dark red, nonluminous | 0.64- 0.79 | −8.03- 5.05 | Devitrification of volcanic glass, acidic dissolution of rock matrix | Burial dolomitization |
| Medium- deep burial | 121-144 | Euhedral, anhedral; fine- crystalline | Metasomatic, fracture-filling, dissolved pore | Green | Orange red, nonluminous | 0.71- 0.97 | −10.54- 2.38 | Dissolution of rock matrix, volcanic hydrothermal fluid | Burial dolomitization, hydrothermal metasomatic dolomitization |
Fig. 9. Formation mechanism of suhedral dolomites in dolomitic rocks of the Fengcheng Formation in the Mahu Sag. |