Introduction
1. System of systems (SOS) and energy system
2. The evolution of world energy system
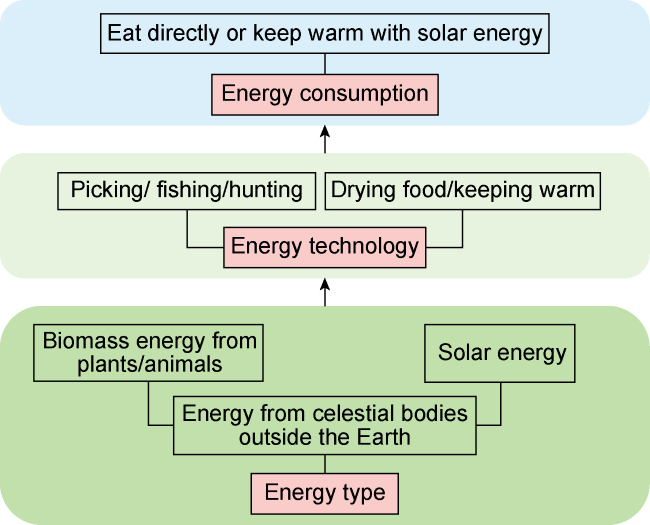
2.1. Primitive energy system
Fig. 1. Diagram of primitive energy system structure. |
Table 1. The characteristics of the energy system and its effect on the industrial system of human society |
| Energy system | Characteristics of energy system | Influence on industrial system | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy supply | Energy technology | Energy structure | Energy storage | Energy management | Industrial system status | Role of energy system | |
| Primitive energy system (250×104 years to 170×104 years ago) | Providing energy with plants and animals | Primitive techniques for maintaining physical strength and body temperature, and saving energy through harvesting, fishing, hunting, and heating | Food for survival | Tribe chief divide food, no energy management system | Beginning of primitive agriculture no industrial system | Survival, promote primitive civilization development, manpower as main energy type | |
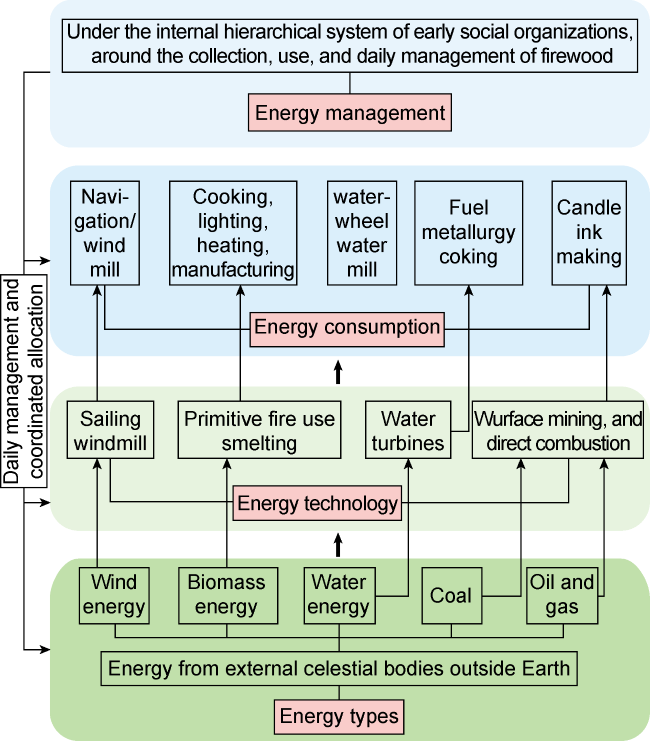
| Ancient energy system (170×104 years to mid 18th century) | Biomass energy, wind energy, hydro energy, etc | Learn to use energy beyond one's own physical strength, master primitive fire technology, and invent techniques for using sails, windmills, and water wheels | Fuelwood as 1st generation main energy source | Fuelwood collection and use regulations under internal hierarchical system of tribes and tribal alliances | Agriculture system formed and dominated, industries and commerce developed from dependent to relatively independent | Promote human evolution and agriculture civilization development, manpower, animal, wind, water as main energy type | |
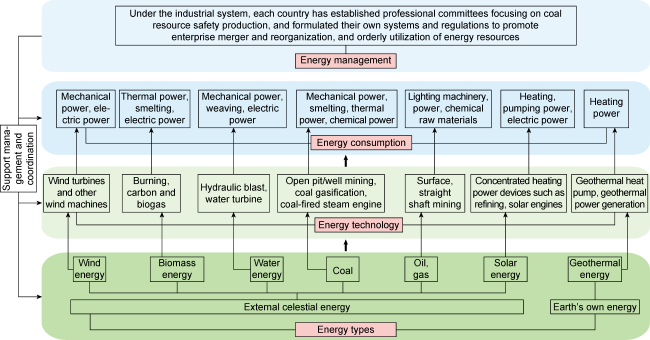
| Modern energy system (1760s — mid 1900s) | Coal, biomass energy, wind energy, hydro energy, solar energy, geothermal energy, etc | Invent technologies such as open-pit/mine coal mining, coal-fired steam engine, hydraulic turbine, wind machinery, etc | Coal as 2nd generation main energy | Initial development of energy storage, mainly lead acid and other chemical batteries for energy storage, no impact on whole systems | Rules and laws for coal development by European and American countries under industrial systems | First, second and third industry gradually formed, industry dominated | Promote human society to contemporary industrial civilization era, steam as main energy source |
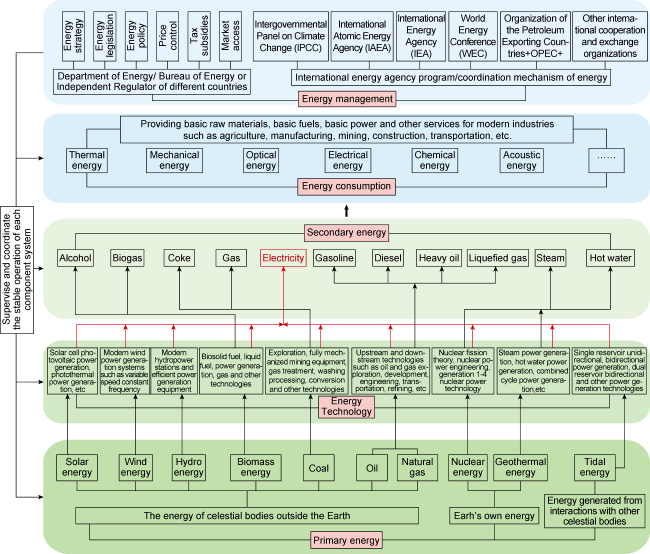
| Contemporary energy system (1960s - now) | Oil, natural gas, coal, hydropower, nuclear energy, solar energy, wind energy, hydrogen energy, biomass energy, etc | Full industry chain technologies such as oil and gas exploration, development, engineering, transportation, refining, coal mining, washing and processing, coal chemical industry, and new energy power generation technology with electricity as the core | Oil and gas as 3rd generation main energy, large sale application of coal, water and nuclear energy | Large-scale development of energy storage technology, nickel-based batteries, lithium-based batteries, pumped energy storage, flywheel energy storage, with impact on energy systems | Modern energy management system established by countries, global energy cooperation coordination system formed | Contemporary industrial systems formed, 1st and 2nd industry synergy and 2nd 3rd industry dual wheel drive to balanced development of three industries | Drive human society to modern civilization, steam, gas, electricity, nuclear as main energy type |
| Green smart energy system (present - mid and late 21th century) | Solar energy, nuclear energy, hydrogen energy, wind energy, hydropower, geothermal energy, biomass energy, tidal energy, natural gas, oil, coal, etc | Synergy technology between new energy, integration and complementary technology between new energy and fossil energy, integrated energy use technology between primary energy and secondary energy, integrated energy service technology of "source network storage", etc | New energy as 4th generation main energy, gradually giving up fossil energy to use nuclear and bioenergy | Energy storage as key component of energy systems, with technology of liquid flow batteries, green hydrogen energy storage, supercapacitor energy storage, superconducting magnetic energy storage, and micro compressed air energy storage | Safe, economical, efficient, clean, low-carbon, intelligent, sustainable global energy governance and cooperation system | Blurred boundaries among three industries, highly intertwined and integrated, new middle industries and cross-border industries dominated by intelligent industry | Promote human society to eco civilization, electricity, nuclear as main energy type |
2.2. Ancient energy system
Fig. 2. Diagram of ancient energy system structure. |
2.3. Modern energy system
Fig. 3. Diagram of modern energy system structure. |
2.4. Contemporary energy system
Fig. 4. Contemporary energy system structure. |
2.5. Green and smart energy system
3. Connotation of green and smart energy system
3.1. Connotation of green and smart energy system
Fig. 5. Green and smart energy systems structure. |
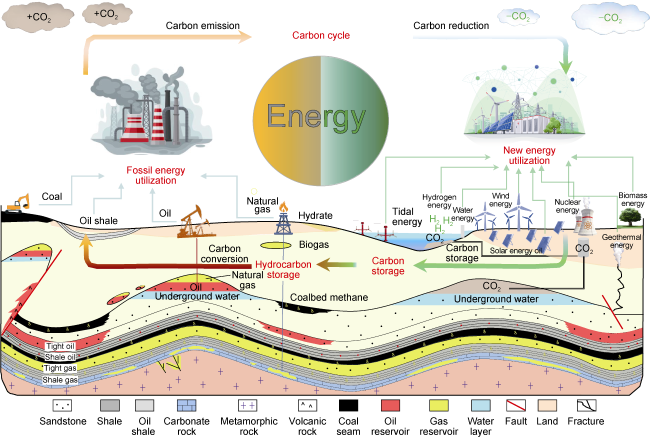
Fig. 6. Energy utilization in the super basin. |
3.2. Operating mechanism of green and smart energy system
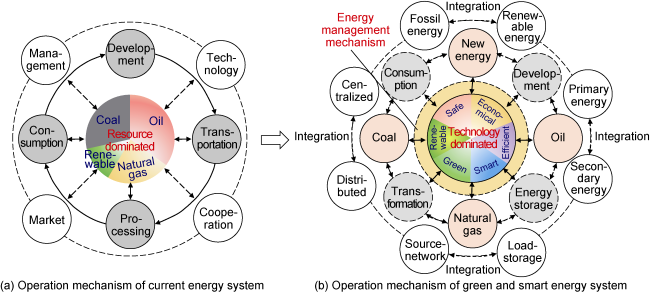
Fig. 7. Overview of the operation mechanism of modern energy system and green smart energy system. |
4. The "six inequalities" of world energy
4.1. Inequal distribution of fossil energy resources in the world
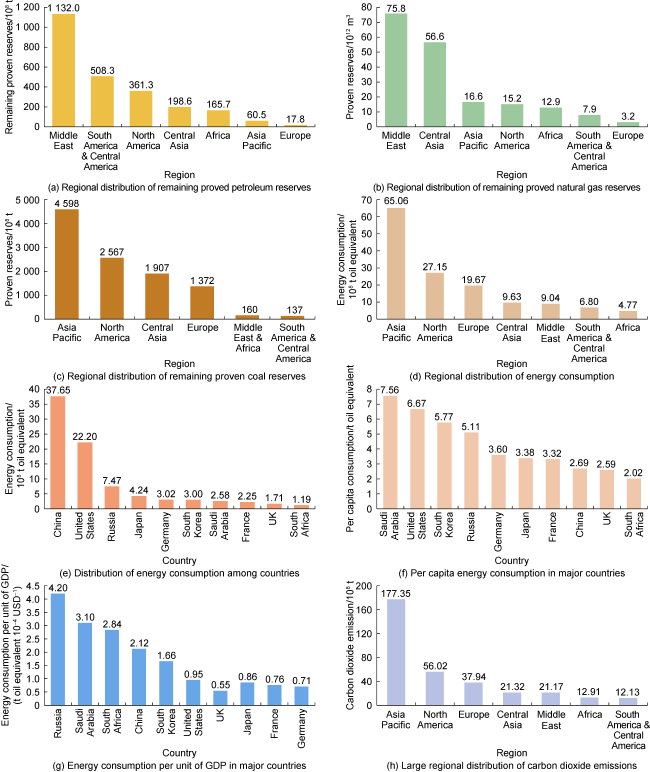
Fig. 8. World major energy remaining proven reserves and consumption, carbon dioxide emissions, and energy consumption per unit of GDP. |
4.2. Inequal world energy consumption in different regions
4.3. Inequal world energy technology development
4.4. Inequal world per capita energy consumption
4.5. Inequal world energy saving
4.6. Inequal carbon emissions of world energy
5. The principles, paths, and measures of China's energy revolution and the construction of a green and smart energy system
5.1. Building a new energy security system that balances resilience and sustainability
5.2. Building a diversified energy production system
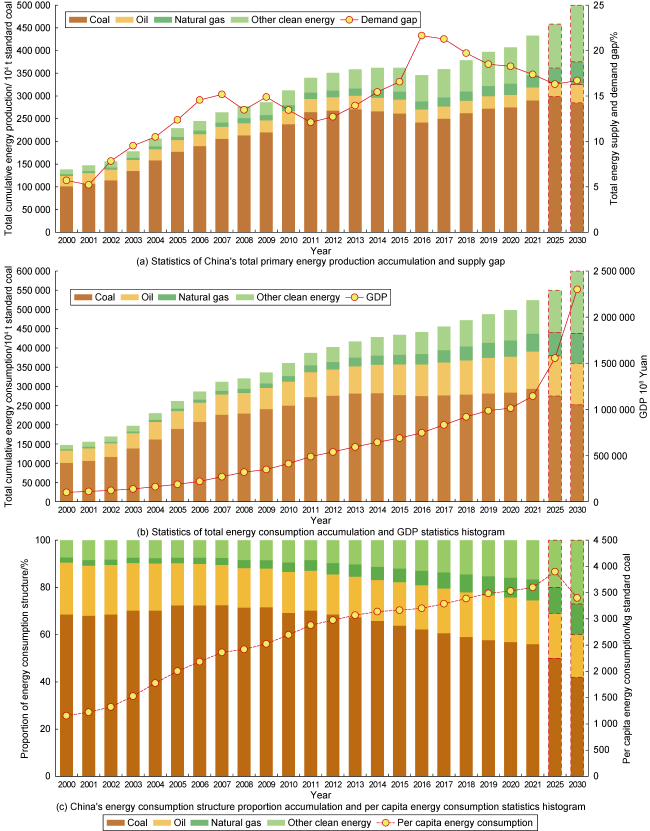
Fig. 9. Statistics of total energy consumption, consumption structure, total energy production in China. |