Introduction
1. Development of key additives for the drilling fluid system
1.1. Weakly cross-linked zwitterionic polymeric fluid loss reducer
1.1.1. Molecular structure design
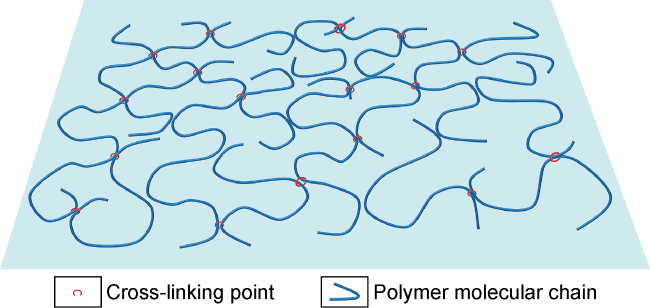
Fig. 1. Schematic illustration of the weakly cross-linked structure of the polymeric fluid loss reducer. |
1.1.2. Evaluation of high-temperature resistance and salt resistance performance
Table 1. Viscosity-improving and fluid loss-reducing performance of DADN in base fluids with different salt contents before and after aging at a high temperature |
| Sample | Condition | Apparent viscosity/ (mPa·s) | Plastic viscosity/ (mPa·s) | API fluid loss/mL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4% Bentonite suspension | Before aging | 9.5 | 7 | 24.8 |
| After aging | 7.0 | 3 | 32.6 | |
| 4% Bentonite suspension + 2% DADN | Before aging | 88.0 | 56 | 4.8 |
| After aging | 17.5 | 14 | 6.0 | |
| 4% Bentonite suspension + 4% NaCl + 2% DADN | Before aging | 44.0 | 32 | 4.0 |
| After aging | 13.0 | 10 | 11.8 | |
| 4% Bentonite suspension + 15% NaCl + 2% DADN | Before aging | 34.0 | 28 | 3.2 |
| After aging | 16.0 | 12 | 8.6 | |
| 4% Bentonite suspension + 36% NaCl + 2% DADN | Before aging | 33.0 | 26 | 3.6 |
| After aging | 19.0 | 15 | 7.4 |
Note: Aging occurred at 200°C for 16 h. |
1.1.3. Salt resistance mechanism
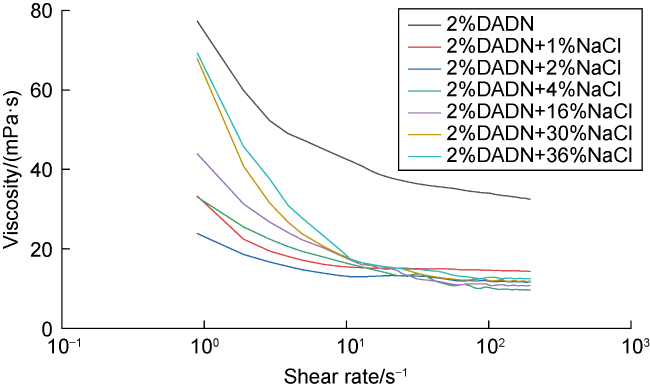
Fig. 2. Effect of the salt content on the viscosity of the DADN aqueous solution. |
1.2. Flexible polymer microsphere nano-plugging agent
1.2.1. Molecular structure design
1.2.2. Characterization
Fig. 3. SEM image and particle-size distribution of the flexible polymer microsphere nano-plugging agent. |
1.2.3. Plugging performance evaluation
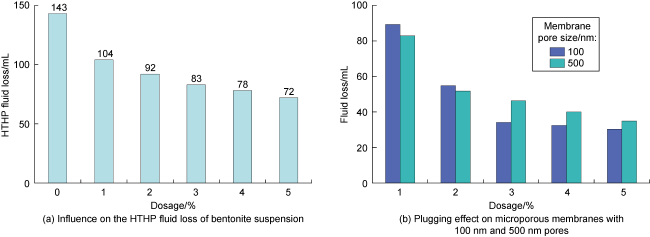
Fig. 4. Performance evaluation of the flexible polymer microsphere nano-plugging agent. |
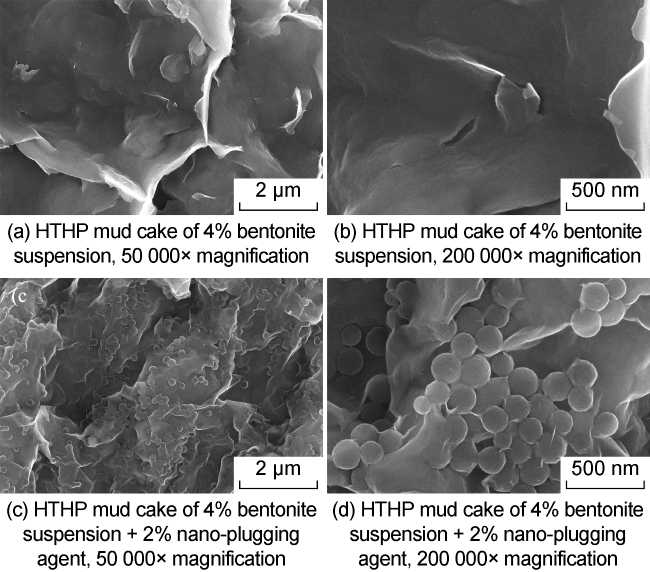
Fig. 5. Influence of the flexible polymer microsphere nano-plugging agent on the microstructure of the HTHP mud cake of the base drilling fluid. |
1.3. Comb-structure polymeric lubricant
1.3.1. Molecular structure design
Fig. 6. (a) Molecular structure and (b) lubrication mechanism of the comb-structure polymeric lubricant (x, y, z represent the number of monomer units in the polymeric lubricant in |
1.3.2. Lubricating performance evaluation
Table 2. Lubricating performance of the comb-structure polymer lubricant in bentonite suspension |
| Sample | Condition | Lubrication coefficient | Reduction rate of lubrication coefficient/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5% bentonite suspension | Unaged | 0.715 5 | |
| 5% bentonite suspension + 1% lubricant | Unaged | 0.064 2 | 91.03 |
| 5% bentonite suspension +35% NaCl | Unaged | 0.389 7 | |
| 5% bentonite suspension +35% NaCl+2% lubricant | Unaged | 0.092 7 | 76.22 |
| 5% bentonite suspension | Aged at 200 °C for 16 h | 0.735 8 | |
| 5% bentonite suspension + 1% lubricant | Aged at 200 °C for 16 h | 0.084 4 | 88.53 |
| 5% bentonite suspension +35% NaCl | Aged at 200 °C for 16 h | 0.564 1 | |
| 5% bentonite suspension +35% NaCl+2% lubricant | Aged at 200 °C for 16 h | 0.129 2 | 77.10 |
2. Construction and performance evaluation of drilling fluid system
2.1. Construction of drilling fluid system
2.2. Experimental methods
2.2.1. Drilling fluid formulation
Table 3. Specifications and effects of drilling fluid additives |
| SN | Additive | Manufacturer | Purity | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bentonite | Huai’an Tengfei Bentonite Development Co., Ltd. | Industrial grade | Adjust rheological properties and reduce fluid loss |
| 2 | Attapulgite | Shandong Deshunyuan Petroleum Sci & Tech. Co., Ltd. | Industrial grade | Reduce fluid loss |
| 3 | Sodium hydroxide | Shandong Deshunyuan Petroleum Sci & Tech. Co., Ltd. | Chemically pure | Adjust pH value |
| 4 | DADN | Laboratory synthesis | 99% | Increase viscosity and reduce fluid loss |
| 5 | Anhydrous polyol | Shandong Deshunyuan Petroleum Sci & Tech. Co., Ltd. | Industrial grade | Reduce fluid loss, inhibit clay hydration, and improve lubricity |
| 6 | Flexible polymer microsphere nano-plugging agent | Laboratory synthesis | Solid content of 30% | Reduce fluid loss and plug micro- pores and fractures |
| 7 | Ultrafine calcium carbonate | Shandong Deshunyuan Petroleum Sci & Tech. Co., Ltd. | Industrial grade | Reduce fluid loss and plugs micro- pores and fractures |
| 8 | Comb-structure polymeric lubricant | Laboratory synthesis | 99% | Improve lubricity |
| 9 | Sodium chloride | Shandong Deshunyuan Petroleum Sci & Tech. Co., Ltd. | Chemically pure | Adjust salinity |
| 10 | Potassium formate | Shandong Deshunyuan Petroleum Sci & Tech. Co., Ltd. | Chemically pure | Improve polymer's temperature resistance |
| 11 | Barite | Sichuan Zhengrong Industrial Co., Ltd. | Industrial grade | Acting as weighting material |
Table 4. Formulations of the drilling fluid system for experimental use |
| Formulation | Dosage | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water/ mL | Bentonite/ g | Attapulgite/ g | Sodium hydroxide/g | Potassium formate/g | DADN/ g | Anhydrous polyol/g | Flexible polymer microsphere nano-plugging agent/g | Ultrafine calcium carbonate/ g | Sodium chloride/ g | Comb- structure polymeric lubricant/g | Barite/ g | |
| A | 400 | 8 | 8 | 0.8 | 20 | 12 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 144 | 12 | 773 |
| B | 400 | 8 | 0 | 0.8 | 20 | 12 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 144 | 12 | 773 |
| C | 400 | 8 | 8 | 0.8 | 20 | 12 | 20 | 0 | 20 | 144 | 12 | 773 |
| D | 400 | 8 | 8 | 0.8 | 20 | 12 | 20 | 20 | 0 | 144 | 12 | 773 |
| E | 400 | 8 | 8 | 0.8 | 20 | 12 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 144 | 0 | 773 |
2.2.2. Evaluation of rheological and filtration properties
2.2.3. Evaluation of sedimentation stability
2.2.4. Evaluation of inhibition performance
2.2.5. Evaluation of plugging performance
2.2.6. Evaluation of lubricating performance
2.3. Results and discussion
2.3.1. Rheological and filtration properties
Table 5. Results of rheological and filtration properties tests of formulations drilling fluids A-E |
| Formulation | Condition | Density/ (g·cm-3) | pH | Apparent viscosity/ (mPa·s) | Plastic viscosity/ (mPa·s) | Yield point/ Pa | YP/PV (Pa·(mPa·s)-1) | Gel strength at 10 s (10 min)/Pa | API fluid loss/mL | HTHP fluid loss/mL | HTHP mud cake thickness/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Before aging | 2.0 | 11 | 116.0 | 92 | 24.0 | 0.26 | 8.0 (11.0) | 0 | ||
| After aging for 16 h | 2.0 | 11 | 114.0 | 96 | 18.0 | 0.19 | 1.5 (3.0) | 1.6 | 14.2 | 3.5 | |
| After aging for 72 h | 2.0 | 11 | 102.0 | 87 | 15.0 | 0.17 | 1.5 (2.5) | 1.8 | 19.6 | 4.5 | |
| B | Before aging | 2.0 | 11 | 113.0 | 75 | 38.0 | 0.51 | 15.0 (16.0) | 0 | ||
| After aging for 16 h | 2.0 | 11 | 104.0 | 93 | 11.0 | 0.12 | 1.0 (2.5) | 2.4 | 52.8 | 7.5 | |
| C | Before aging | 2.0 | 11 | 94.5 | 68 | 26.5 | 0.39 | 3.5 (12.0) | 1.0 | ||
| After aging for 16 h | 2.0 | 11 | 80.5 | 68 | 12.5 | 0.18 | 2.0 (2.5) | 2.0 | 32.0 | 4.5 | |
| D | Before aging | 2.0 | 11 | 89.5 | 62 | 27.5 | 0.44 | 6.5 (14.0) | 0 | ||
| After aging for 16 h | 2.0 | 11 | 100.5 | 83 | 17.5 | 0.21 | 2.5 (5.0) | 1.0 | 36.4 | 5.0 | |
| E | Before aging | 2.0 | 11 | 105.0 | 82 | 23.0 | 0.28 | 6.5 (11.0) | 0 | ||
| After aging for 16 h | 2.0 | 11 | 98.0 | 84 | 14.0 | 0.17 | 1.5 (3.0) | 1.6 | 28.2 | 4.5 |
Note: Aging was completed at 200 °C, and the test of HTHP fluid loss was performed at 200 °C and 3.5 MPa. |
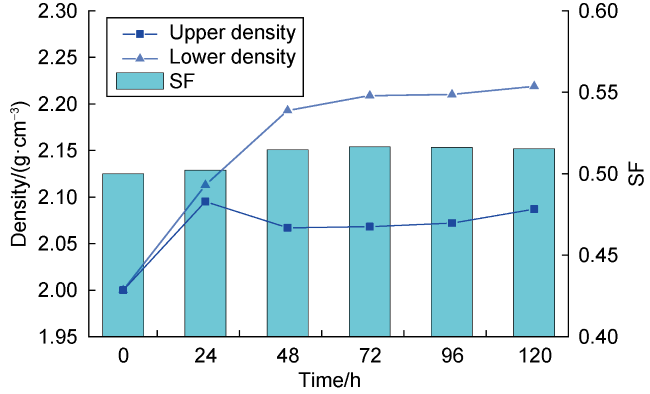
2.3.2. Sedimentation stability
Fig. 7. SF of the drilling fluid system after aging at 200 °C for different time. |
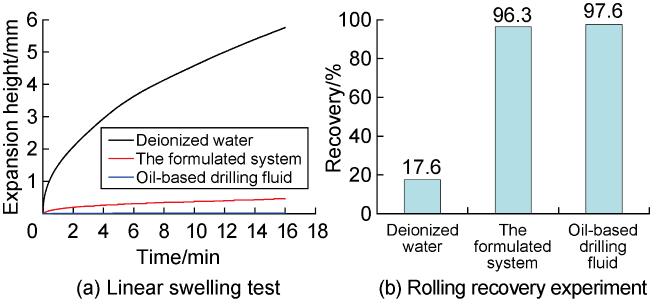
2.3.3. Inhibition performance
Fig. 8. Evaluation results for the inhibition performance of drilling fluid systems. |
2.3.4. Plugging performance
Fig. 9. Evaluation results for the plugging performance of the drilling fluid system. |