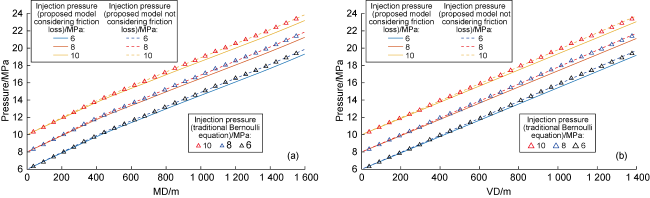
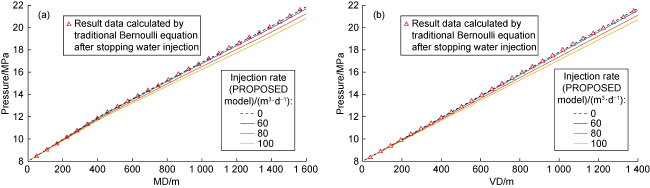
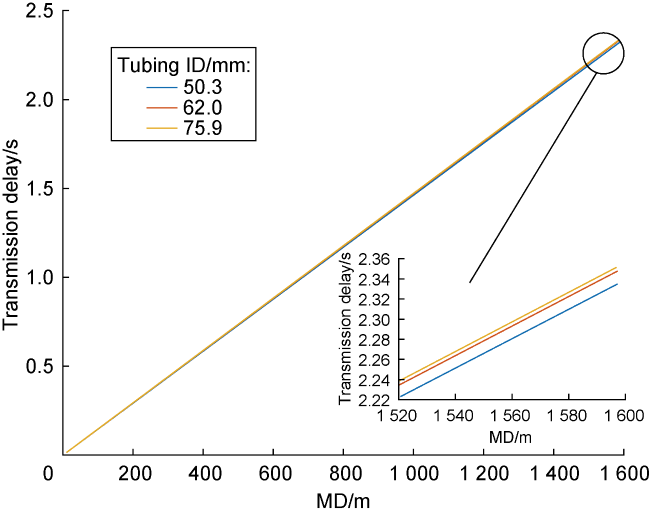
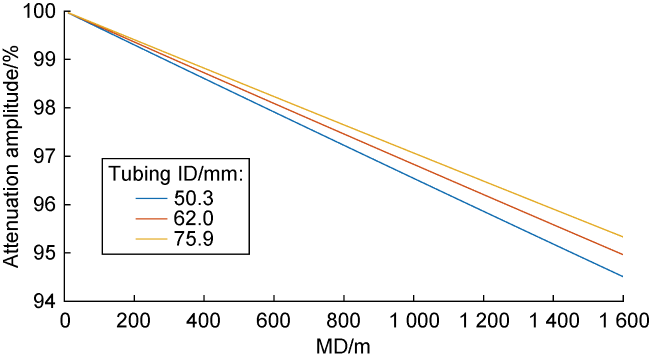
a—acceleration of fluid microelement motion, m/s2;
a—acceleration matrix of a hexahedron microelement, m/s2;
a0—coefficient of normal stress term on fluid microelement, dimensionless;
b0—coefficient of constitutive relationship term for fluid microelement, dimensionless;
A—cross-sectional area of tubing, m2;
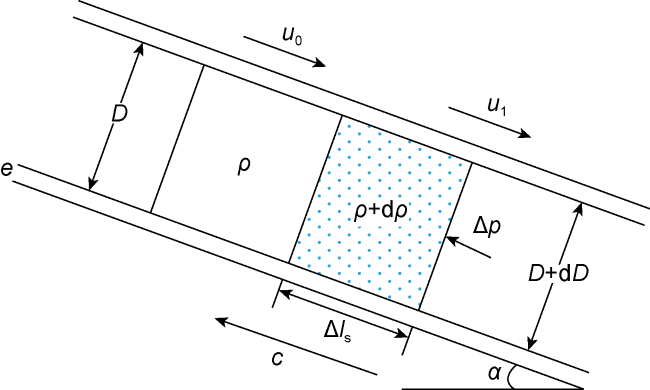
c—fluid wave propagation velocity, m/s;
e—thickness of tubing wall, m;
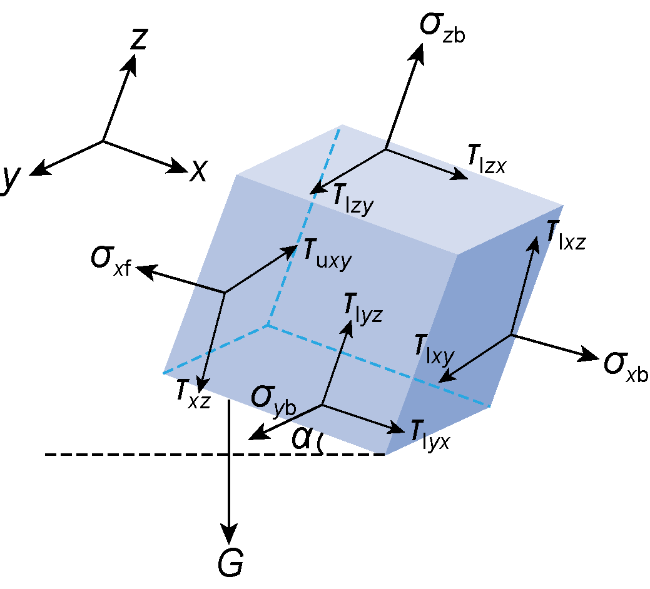
eσ—normal stress matrix of a moving fluid microelement, Pa;
$\overline{{{e}_{\sigma }}}$—normal stress matrix of a static fluid microelement, Pa;
eτ—constitutive tangential stress matrix of a fluid microelement, Pa;
eστ—resultant stress on a fluid microelement, Pa;
E—elastic modulus of fluid, Pa;
E0—elastic modulus of tubing, Pa;
f—fluid wave frequency, Hz;
F—resultant force on a fluid microelement, N;
g—gravitational acceleration, m/s2;
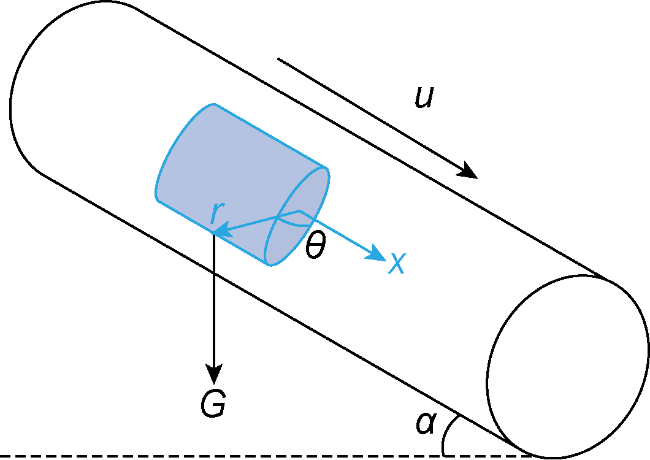
G—gravity matrix of a fluid microelement, N;
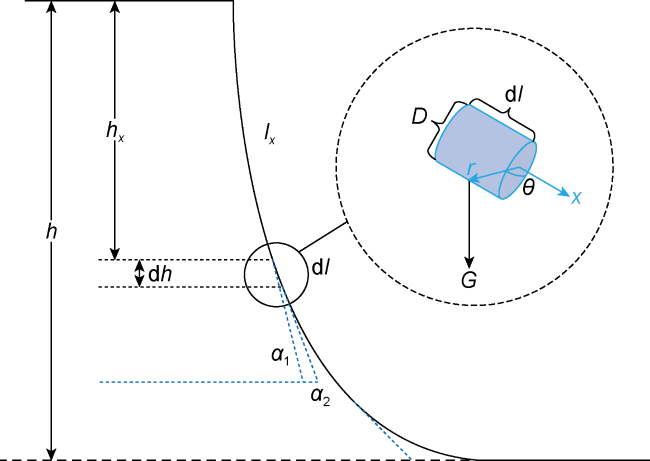
h—vertical depth of a whole well, m;
hx—vertical depth at a point in a wellbore, m;
k—formation water absorption index, m3/(s•Pa);
kε—material coefficient, dimensionless;
l—measured depth of a whole well, m;
lx—measured depth at a point in a wellbore, m;
Δls—length of the flow section with water hammer effect, m;
pb—formation opening pressure, Pa;
ph—bottom hole pressure, Pa;
px—pressure at lx from the wellhead, Pa;
p0—wellhead pressure, Pa;
p1—inlet pressure of the micro-section, Pa;
p2—outlet pressure of the micro-section, Pa;
qv—volume flow rate, m3/s;
Δp—pressure difference, Pa;
Δpe—fluid pressure drop per unit length of wellbore, Pa/m;
Δpx—pressure wave amplitude at lx, Pa;
Δpl—pressure amplitude at the throttling element, Pa;
r—radial distance in a cylindrical coordinate system, m;
Re—Reynolds number, dimensionless;
T—period of pulse signal, s;
u—fluid rate matrix of a hexahedron microelement, m/s;
$\bar{u}$—average flow rate, m/s;
u0, u1—flow rate before and after fluid compression, m/s;
ΔV—volume of the flow section, m3;
x, y, z—Cartesian coordinate system, m;
Z—practical conductivity coefficient, m4/(s•Pa);
Z0—conductivity coefficient of continuous tubing, m4/(s•Pa);
α—angle between fluid microelement and horizontal direction, (°);
α1—angle between the tangent line at the inlet of the well section and the horizontal line, (°);
α2—angle between the tangent line at the outlet of the well section and the horizontal direction, (°);
δx—signal attenuation coefficient, dimensionless;
θ—polar angle in cylindrical coordinate system, (°);
σ—normal stress on a fluid microelement, Pa;
σp—normal stress matrix on a fluid microelement, Pa;
σp—normal stress on the stress surface of a static fluid microelement, Pa;
σxb, σyb, σzb—normal stresses perpendicular to the stress surface of the microelement generated by the back microelement at x, y, z axis, Pa;
σxf, σyf, σzf—normal stresses perpendicular to the stress surface of the microelement generated by the front microelement at x, y, z axis, Pa;
τ—tangential stress on a fluid microelement, Pa;
τq—tangential stress matrix on a fluid microelement, Pa;
τxy, τxz—tangential stresses generated by deformation in x direction on y and z directions, Pa;
τyx, τyz—tangential stresses generated by deformation in y direction on x and z directions, Pa;
τzx, τzy—tangential stresses generated by deformation in z direction on x and y directions, Pa;
ϕ—angle between a well section and the horizontal line, which is a function of well MD and VD, (°).
u, l—top and bottom surfaces of a microelement perpendicular to the axis;