Introduction
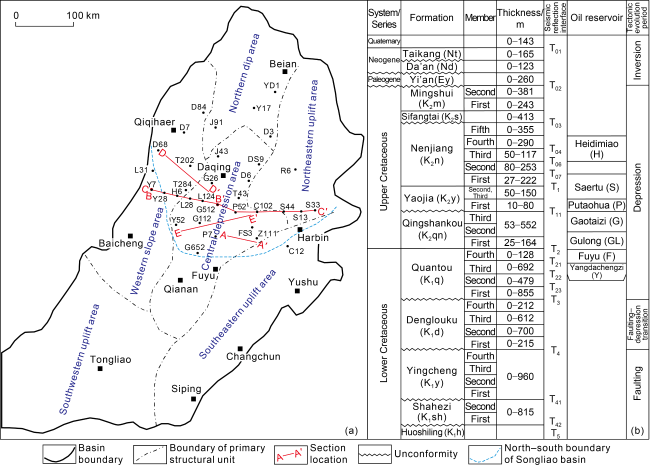
1. Geological setting
Fig. 1. (a) Structural unit division and (b) comprehensive stratigraphic column of Songliao Basin. |
2. Formation conditions of the whole petroleum system
2.1. High-quality source rocks provided sufficient petroleum sources
2.2. Multiple types of reservoirs provided varied storage spaces
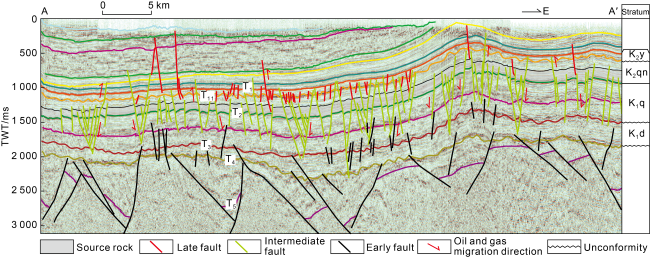
2.3. Alternating presence of small faults near the source and large faults far from the source was beneficial for the preservation of various petroleum resources
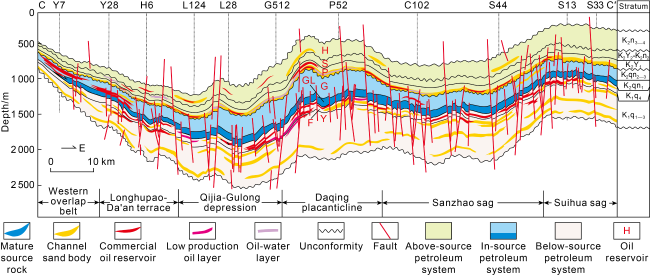
Fig. 2. Shallow-medium seismic section of northern Songliao Basin (see the section position in |
3. Petroleum distribution in the whole petroleum system
3.1. Correlation and differences between various reservoirs
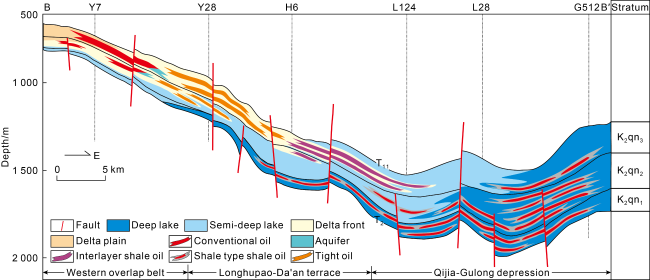
3.1.1. Orderliness and differences of sedimentary systems
Fig. 3. Reservoir section of Qingshankou Formation in Yingtai-Gulong area, northern Songliao Basin (k2qn1—first member of Upper Cretaceous Qingshankou Formation, k2qn2—second member of Upper Cretaceous Qingshankou Formation, k2qn3—third member of Upper Cretaceous Qingshankou Formation; see the section position in |
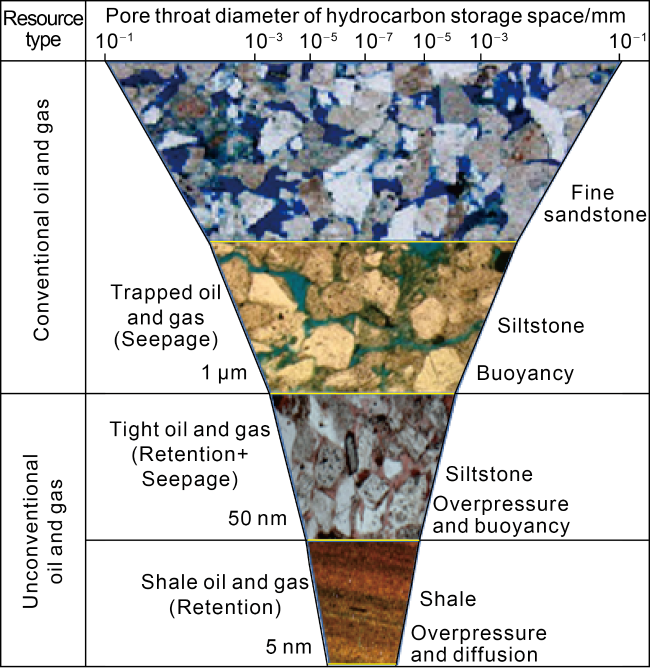
3.1.2. Orderliness and differences of lithology and physical properties
Fig. 4. Scale of storage space by reservoirs in shallow- medium strata in northern Songliao Basin. |
3.2. Orderly distribution of petroleum resources
3.2.1. Longitudinal distribution
Fig. 5. Longitudinal distribution of conventional and unconventional petroleum in shallow-medium strata in northern Songliao Basin. k2n2—second member of Upper Cretaceous Nenjiang Formation, k2n3—third member of Upper Cretaceous Nenjiang Formation, k2n4—fourth member of Upper Cretaceous Nenjiang Formation, k2y1—first member of Upper Cretaceous Yaojia Formation, k2y2—second member of Upper Cretaceous Yaojia Formation, k2q1-3—1st-3nd members of Lower Cretaceous Quantou Formation, k2q4—fourth member of Lower Cretaceous Quantou Formation. |
3.2.2. Planar distribution
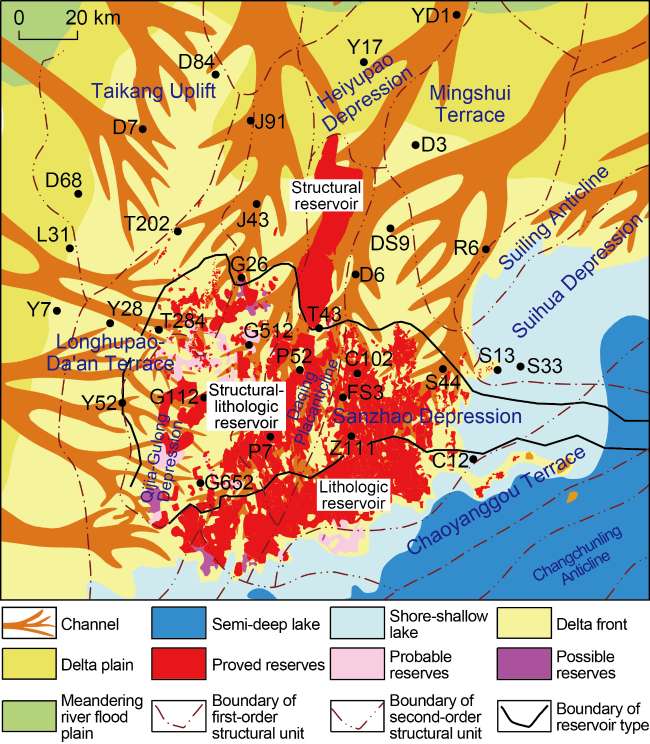
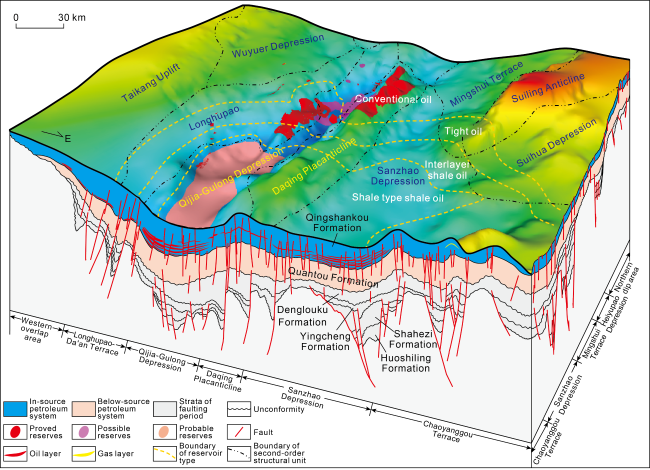
Fig. 6. Above-source petroleum distribution in shallow- medium strata in northern Songliao Basin. |
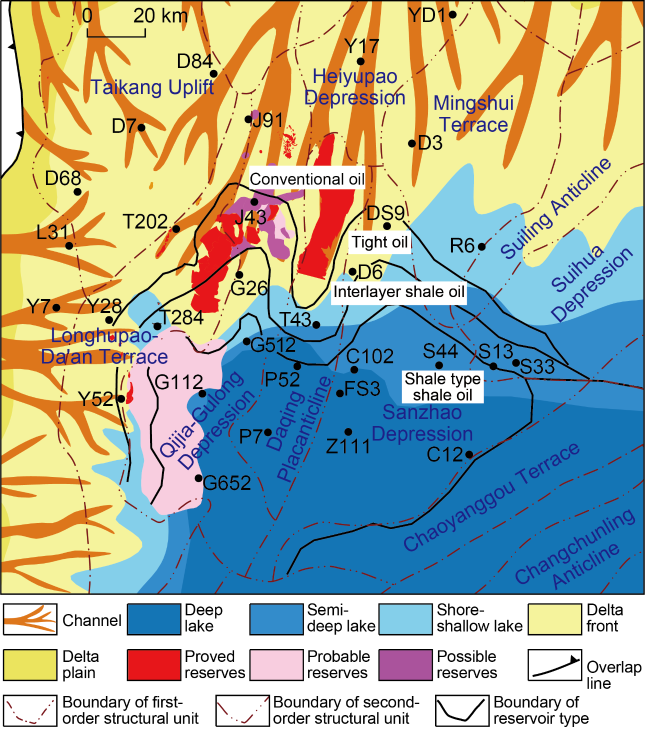
Fig. 7. In-source petroleum distribution in shallow- medium strata in northern Songliao Basin. |
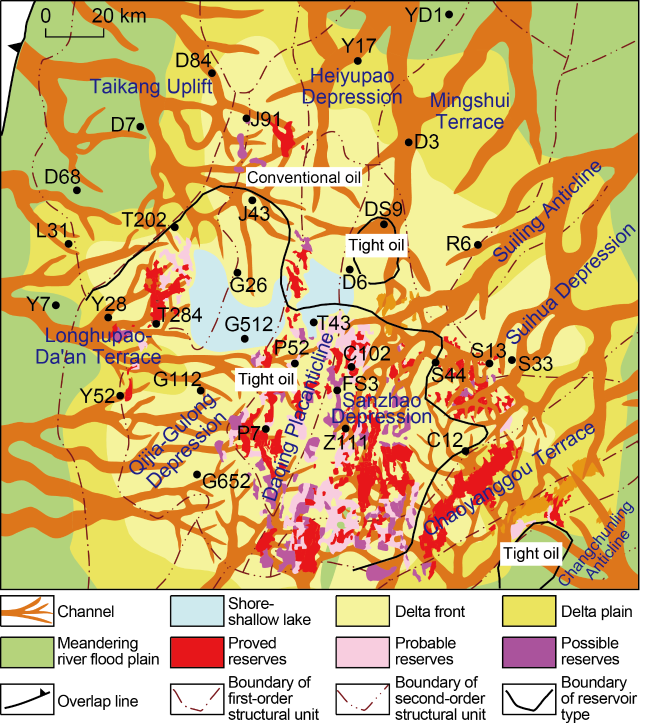
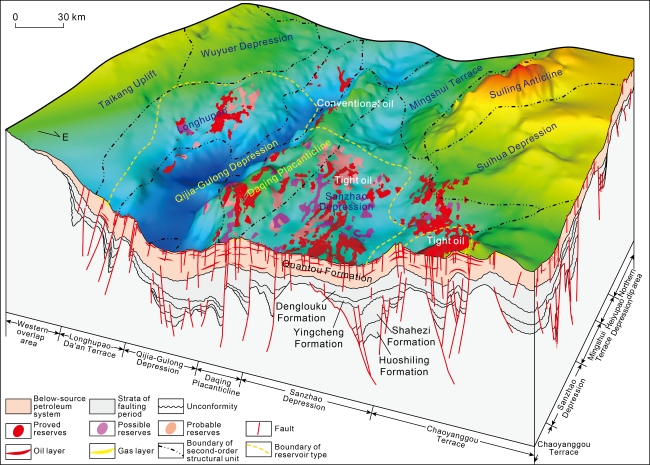
Fig. 8. Below-source petroleum distribution in shallow- medium strata in northern Songliao Basin. |
4. Petroleum accumulation and distribution models in the whole petroleum system
Table 1. Characteristics of conventional oil, tight oil and shale oil reservoirs in the whole petroleum system in the shallow- medium strata, northern Songliao Basin |
| Reservoir type | Structural units | Sedimentary facies | Lithology | Accumulation model | Accumulation mechanism | Migration characteristics | Driving force | Resistance | Spatial location relative to the source | Fluid features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional oil | Structural high, uplift between depressions, nosing structure | Delta plain, delta front, shore-shallow lake, semi- deep lake | Fine sandstone, siltstone, etc. | Source and reservoir separated, accumulation by buoyancy-driven charging | Closure | Secondary migration | Buoyancy | Gravity | Far from the source | Differential oil and gas |
| Tight oil | Marginal slope area of depression, nosing structure, uplift area in depression | River, delta plain, delta front, shore- shallow lake | Fine sandstone, siltstone, argillaceous siltstone, etc. | Source and reservoir in close proximity, accumulation by source- reservoir pressure difference-driven charging | Stayed | Primary migration or short- distance secondary migration | Source- reservoir pressure difference, buoyancy | Capillary resistance | Near the source | No unified oil-water contact, continuous distribution in large area |
| Shale oil | Depressed area | Delta front, semi-deep lake, deep lake | Shale, sandstone interlayer, dolomite interlayer, etc. | Source and reservoir integrated, accumulation by retention | Retention, stayed | No migration or Micro- migration | Pressure induced by hydrocarbon generation | Capillary resistance, viscous force, friction force | Inside the source |
4.1. Conventional oil accumulation by buoyancy-driven charging above the source
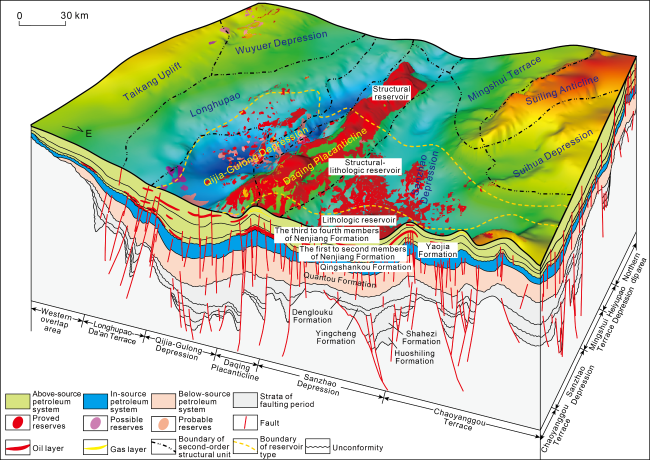
Fig. 9. Three-dimensional superposition of reserves in Heidimiao, Saertu and Putaohua reservoirs above the source in shallow-medium strata in northern Songliao Basin. |
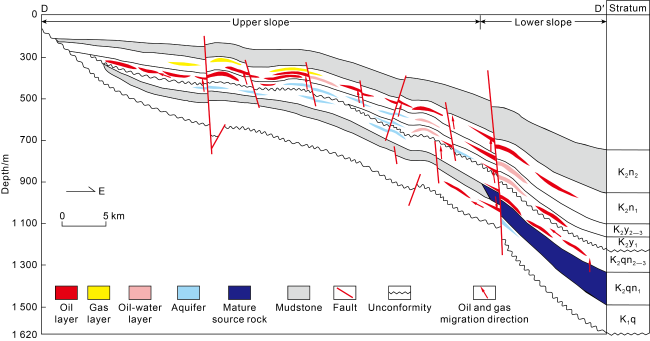
Fig. 10. Petroleum accumulation model of shallow-medium strata in western slope of northern Songliao Basin (see the section position in |
4.2. Shale oil accumulation by retention inside the source
Fig. 11. Petroleum distribution and reserves superimposition of Qingshankou Formation inside the source in shallow- medium strata in northern Songliao Basin. |
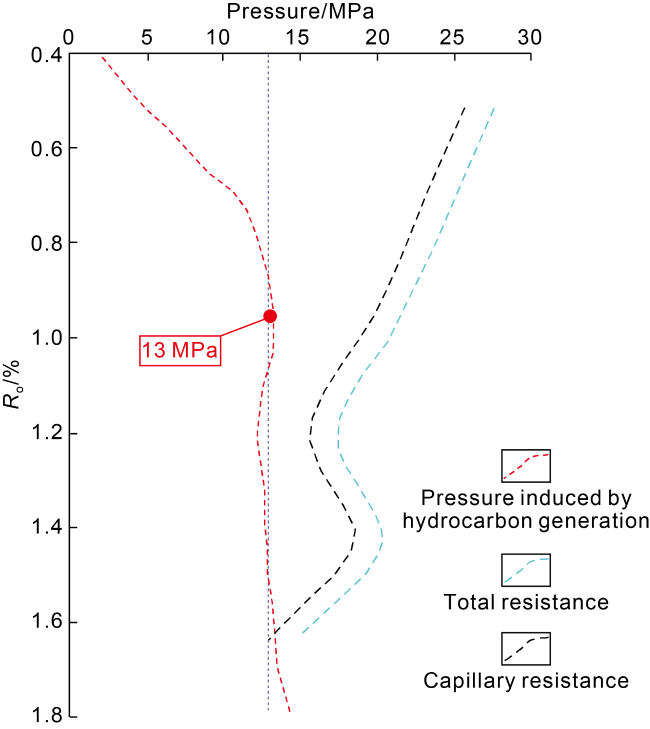
Fig. 12. Relationship between pressure induced by hydrocarbon generation and resistance in shale oil reservoirs in northern Songliao Basin. |
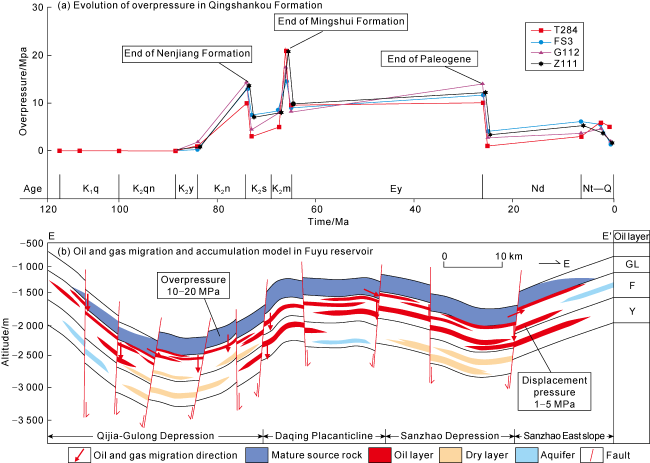
4.3. Tight oil accumulation by source-reservoir pressure difference charging below the source
Fig. 13. Petroleum distribution and reserves superimposition in Fuyu and Yangdachengzi reservoirs in shallow-medium strata in northern Songliao Basin. |
Fig. 14. Mechanism of below-source tight oil and gas charging in shallow-medium strata in northern Songliao Basin (see the section position in |