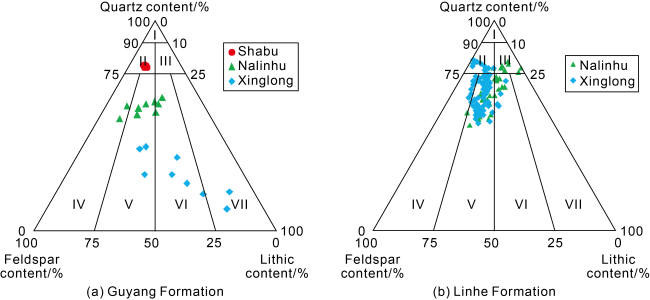
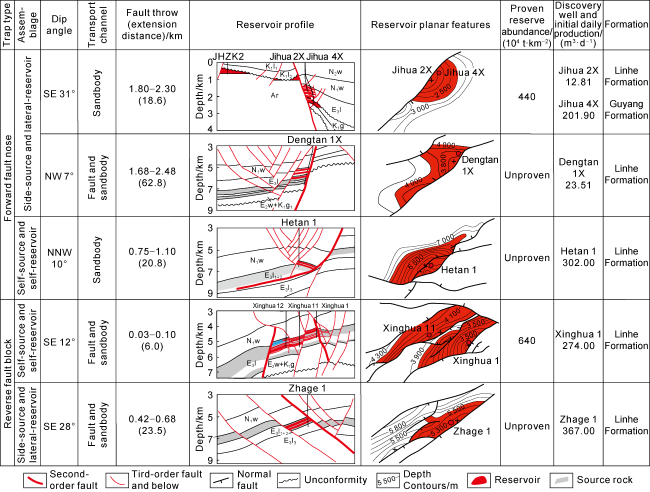
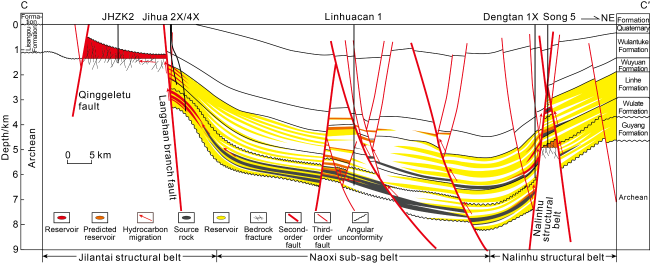
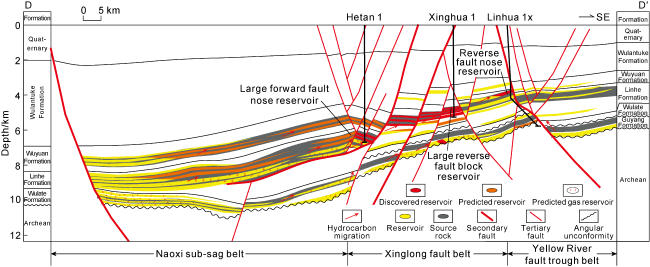
There are mainly three sets of source rocks developed in the Linhe Depression, which are the Lower Cretaceous Gu 2 Member (K
1g
2), Gu 1 Member (K
1g
1) and Oligocene Linhe Formation (E
3l). In the early basin, the Gu 2 Member source rock was mainly distributed in the northern part of the Linhe Depression, with high organic matter abundance and Type II
2 and Type III kerogen, and deposited in freshwater and weak reduction environment
[9]. The source rocks of the Gu 1 Member and Linhe Formation were widely distributed, with higher organic matter abundance and types I and II
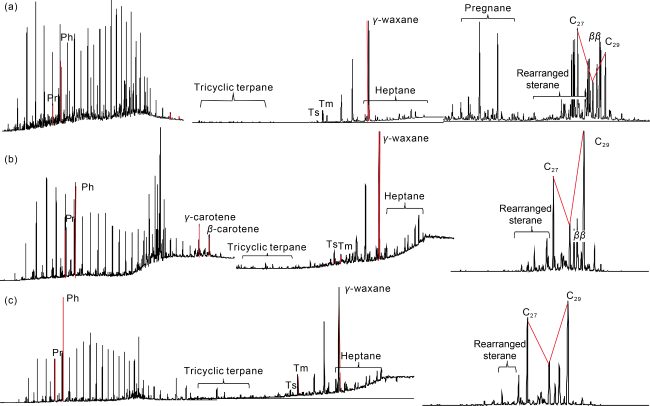
1 kerogen. Geochemical indicators show high boron content, low pristane-to-phytane ratio, and high gammacerane (value of gammacerane/C
30 hopane greater than 1) (
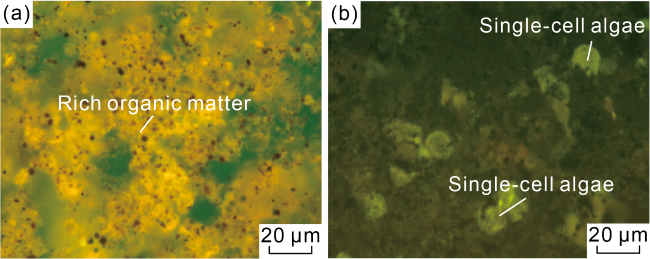
Fig. 6a, 6b). The microscopic fraction of kerogen contains more than 70% of sapropelinite and less than 10% of vitrinite, and microscopic fluorescence irradiation revealed rich algae, mostly unicellular alga (
Fig. 7). In addition, pyrite was found, and the highest content of reduced sulfur in organic carbon reached 6%, reflecting a fully closed and strongly reduced water environment. It’s a salt/saline lake environment with strongly reducing conditions, and very similar to the salt/saline lakes where source rocks were developed in the Qaidam Basin, Jianghan Basin, and Bohai Bay Basin
[12⇓⇓-15]. The K
1g
1 source rock was deposited in shallow lake water (0.5-2.0 m) with a little water supply and high salinity. The sterane/hopane ratio was 1%-10%, the organic matter was from low aquatic prokaryotes (bacteria), and the biological population was simple halophilic bacteria, with little inter-population phagocytosis consumption, and extremely high biological productivity. Gold tube thermal simulation shows that the source rock may start generate massive hydrocarbon when R
o is 0.4%, and reaches peak hydrocarbon generation when R
o is 0.8%, which is much earlier than the source rocks of other basins, revealing a strong hydrocarbon generation ability of the K
1g
1 source rock. Compared with K
1g
1, pregnane is less developed and carotene is more developed in the source rock of the Linhe Formation, especially that the content of
γ-carotane is higher than that of
β-carotane (
Fig. 6b). The latest study indicates that green sulphur bacteria dominate in the Oligocene paleolake and contribute more to carotenoids. The sterane/hopane ratio of 10%-20% indicates that the organic matter was mainly lower aquatic eukaryotes (plankton), and a small amount of terrestrial debris with high biological productivity. Thermal simulation indicates that the peak hydrocarbon generation rate is 730-790 kg/t
[3], revealing a strong hydrocarbon generation ability of the Linhe source rock. According to the comparison of oil sources and the analysis of crude oil maturity, the crude oil of the Linhe Formation in the Xinglong fault belt and the Nalinhu fault buried-hill belt came from the source rock of the Linhe Formation. And based on the maturity index (isomerization index) of C
29, it is found that the crude oil of the Linhe Formation is immature and low mature. For example, the C
29-20
S/(20
S+20
R) found in Well Song5 is only 16.47%, indicating the crude oil is immature (
Fig. 6c). However, the physical properties of the crude oil is mature, with the density of 0.879 g/cm
3, viscosity of 38 mPa∙s, wax content of 14%, sulfur content of 0.71%, freezing point of 33 °C, and asphaltene gum content of 29%. In addition, the C
29-20
S/(20
S+20
R) of the reservoirs in wells Linhua1X and Xinghua1 is 20%-30%, indicating the crude oil is in the low maturity stage (C
29-20
S/(20
S+20
R is 20%-40%), but the physical properties of the crude oil show mature characteristics. The maturity analysis of source rock at 3000-7000 m concludes that the hydrocarbon generation window of the Linhe Formation source rock is 4000- 5000 m, which is significantly deeper than those in other basins in China
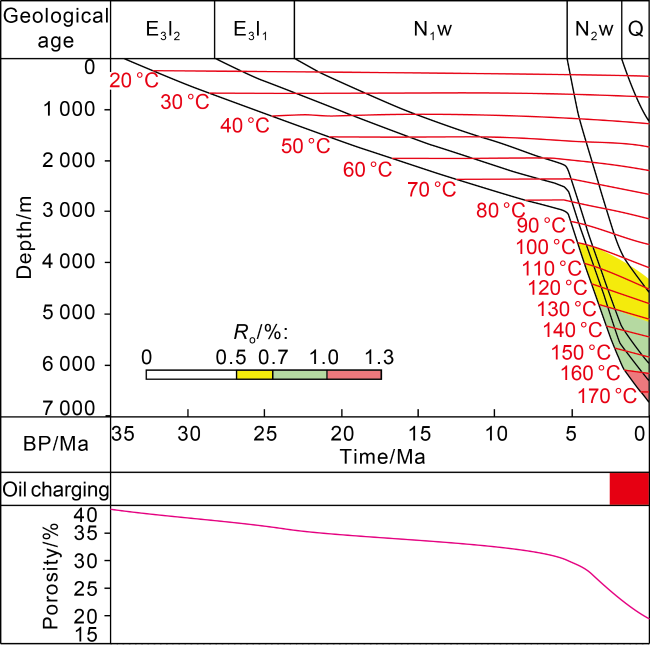
[16-17]. Therefore, it is concluded that the source rock of the Linhe Formation has characteristics of high sulfur and rich algae, early maturity and discharge, and a wide hydrocarbon generation window. The latest hydrocarbon resource estimate is 2-3 times higher than the early, which greatly expands the exploration potential of the Hetao Basin.