Introduction
1. Overview
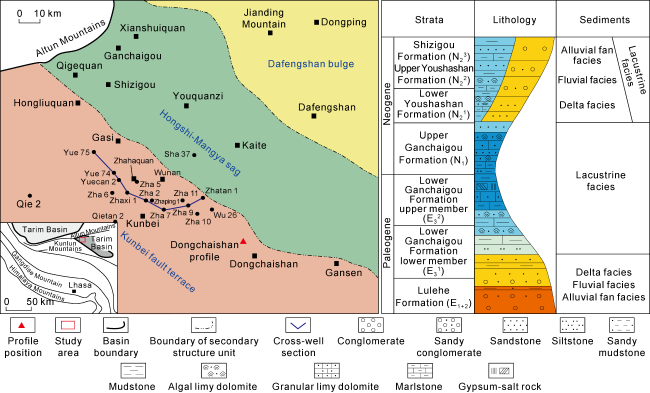
Fig. 1. Location of the study area and composite histogram of the southwestern Qaidam Basin. |
2. Sedimentary characteristics of beach-bar sandstone of saline lake facies
2.1. Sedimentary lithofacies assemblages of beach-bar sandstones
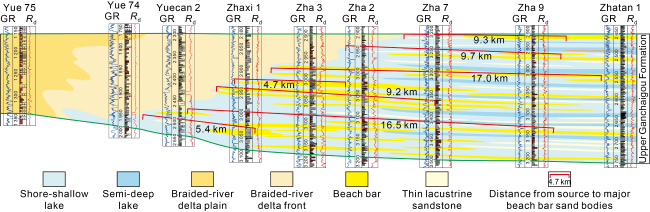
Fig. 2. Sedimentary characteristics of the Neogene Upper Ganchaigou Formation on Dongchaishan section. |
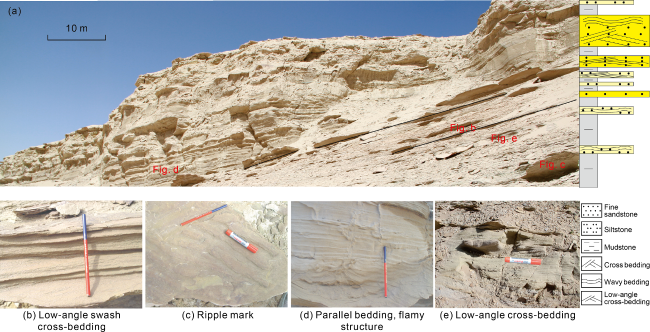
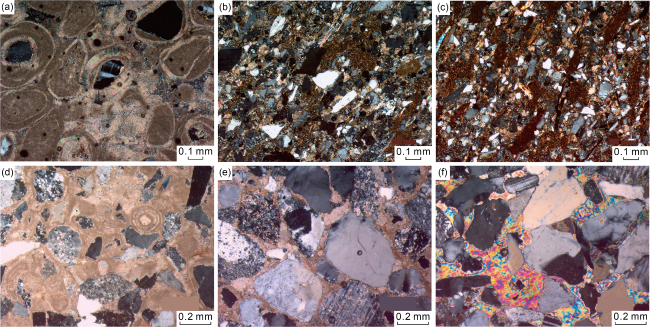
Fig. 3. Typical sedimentary phenomena of Neogene beach-bar sandstones in southwestern Qaidam Basin. (a) Well Zhaping1, 3273.00-3274.80 m, fine sandstone, low-angle cross-bedding; (b) Well Zhaping1, 3277.20-3277.35 m, fine sandstone, low-angle cross-bedding; (c) Well Zha2, 3125.93-3126.12 m, fine sandstone, low-angle cross-bedding; (d) Well Zhaping1, 3277.30-3277.42 m, fine sandstone, low-angle cross-bedding - wave ripple bedding; (e) Well Zhaping1, 3283.80-3283.88 m, siltstone, low-angle cross-bedding - wave ripple bedding; (f) Well Zhaping1, 3249.60-3249.65 m, siltstone, wave ripple bedding; (g) Well Zhaping1, 3465.98-3466.20 m, fine sandstone, wavy-vein bedding; (h) Well Zhaping1, 3409.69-3409.81 m, siltstone, wavy-lenticular bedding. |
2.2. Sedimentary cycle patterns of saline lake beach-bar sandstones
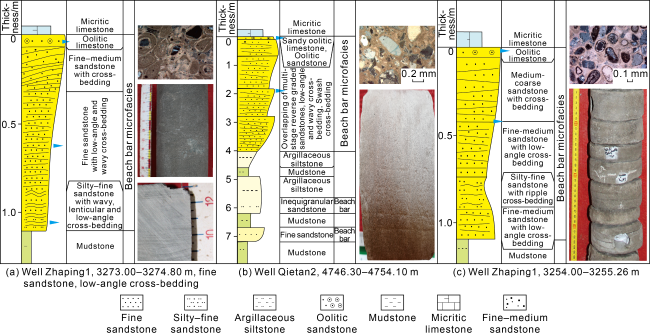
Fig. 4. Typical sedimentary sequences of the beach-bar sandstone of the Upper Ganchaigou Formation in Zhahaquan area. |
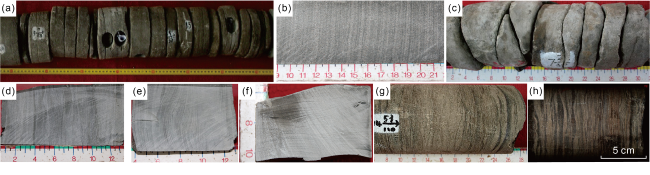
Fig. 5. Typical photos of sedimentary cycles of beach bars in Zhahaquan area (under cross-polarized light, x100). (a) Well Zhaping1, 3242.68 m, oolitic limestone; (b) Well Zhaping1, 3244.37 m, lime-bearing inequigranular feldspar sandstone; (c) Well Zhaping1, 4744.44 m, lime-bearing silty-very fine feldspar sandstone; (d) Well Qieshen2, 4743.54 m, calcarenitic oolitic limestone; (e) Well Qieshen2, 4743.73 m, lime-bearing medium-coarse feldspar lithic sandstone; (f) Well Qieshen2, 4744.44 m, gypsum-bearing fine-medium lithic feldspar sandstone. |
2.3. Development of beach-bar sandstone in saline lake basin
2.3.1. Cross-well section of saline lake basin beach bars
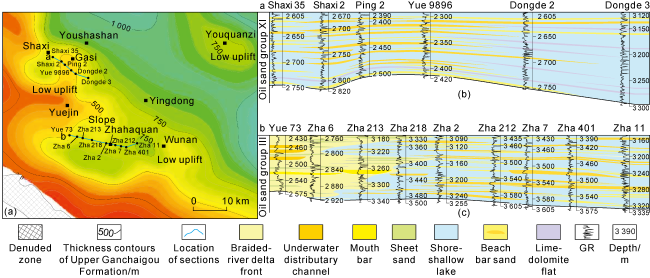
Fig. 6. W-E cross-well section of the Upper Ganchaigou Formation in the Yuejin-Zhahaquan area, southwestern Qaidam Basin (see section position in |
2.3.2. Planar distribution of saline lake basin beach bars
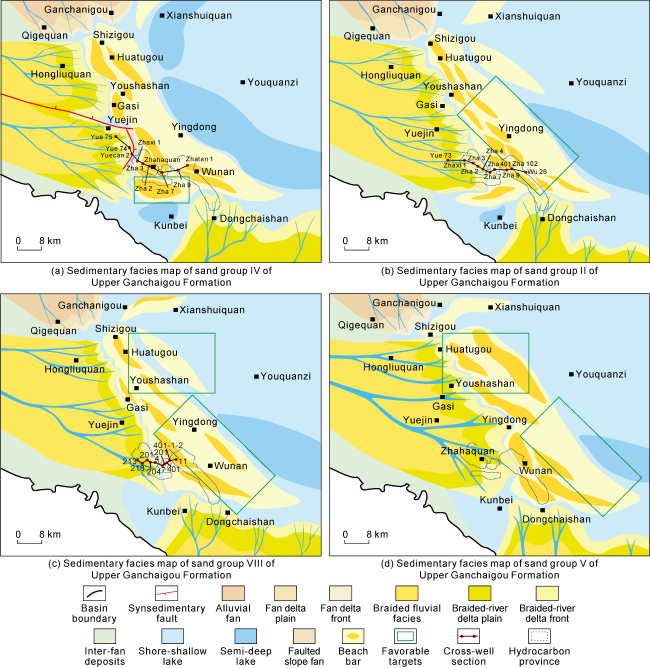
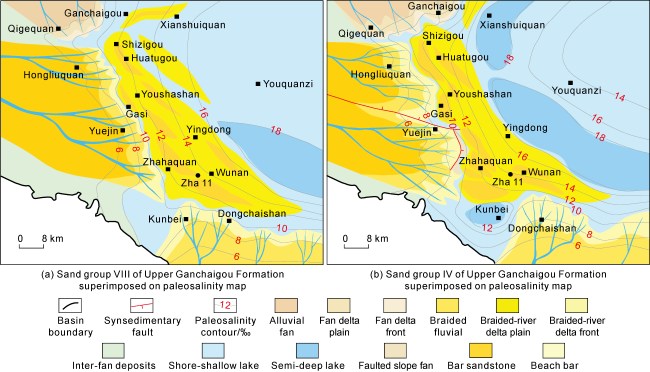
Fig. 7. Sedimentary facies map of some sand groups in the Upper Ganchaigou-Lower Youshashan formations, southwestern Qaidam Basin. |
3. Controlling factors of the development of saline lake basin beach-bar sandstone
3.1. Water salinity controls the sedimentation rate and offshore distance of beach-bar sandstone
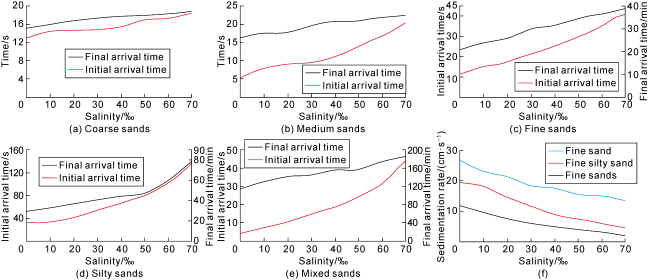
Table 1. Sedimentation rates of different-grained samples at different salinities |
| Salinity/‰ | Initial time when some particle reaches the bottom/s | Final time when all particle reaches the bottom/s | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coarse sands | Medium sands | Fine sands | Coarse silty sand | Mixed sands | Coarse sands | Medium sands | Fine sands | Coarse silty sand | Complex sand | |
| 0 | 13.01 | 16.30 | 23.37 | 31.77 | 28.56 | 15.10 | 5.23 | 10.01 | 28.68 | 16.21 |
| 10 | 14.46 | 17.55 | 26.78 | 33.66 | 32.32 | 15.90 | 7.62 | 13.12 | 32.34 | 29.00 |
| 20 | 14.66 | 17.86 | 29.04 | 41.56 | 35.04 | 16.70 | 8.91 | 15.33 | 36.55 | 41.12 |
| 30 | 14.95 | 19.55 | 33.63 | 52.87 | 36.20 | 17.20 | 9.42 | 19.11 | 39.79 | 58.89 |
| 40 | 15.43 | 20.75 | 35.23 | 69.04 | 38.91 | 17.80 | 11.15 | 22.23 | 43.94 | 74.23 |
| 50 | 16.78 | 20.95 | 38.78 | 82.72 | 39.38 | 17.90 | 14.09 | 26.36 | 46.88 | 97.18 |
| 60 | 17.26 | 21.82 | 40.48 | 102.31 | 43.28 | 18.20 | 16.78 | 31.19 | 58.46 | 125.24 |
| 70 | 18.27 | 22.46 | 41.02 | 143.71 | 46.25 | 18.80 | 20.44 | 38.46 | 78.11 | 186.27 |
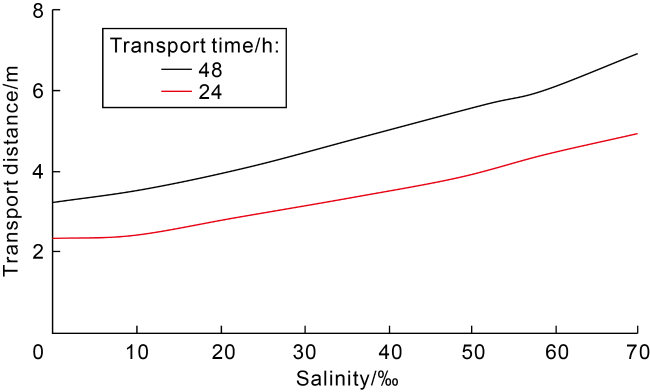
Fig. 8. Sedimentation rates of different grains at different salinities. |
Table 2. Sedimentation rates and transport distances of different-grained samples at different salinities |
| Salinity/‰ | Average sedimentation rate/(cm•s-1) | Transport distance/m | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fine sand | Coarse silty sand | Fine silty sand | 24 h | 48 h | |
| 0 | 26.68 | 19.47 | 11.89 | 2.34 | 3.21 |
| 10 | 23.17 | 18.14 | 9.80 | 2.41 | 3.53 |
| 20 | 21.31 | 14.71 | 7.44 | 2.79 | 3.92 |
| 30 | 18.37 | 11.60 | 6.13 | 3.12 | 4.46 |
| 40 | 17.48 | 8.92 | 5.10 | 3.51 | 4.99 |
| 50 | 15.43 | 7.47 | 4.17 | 3.89 | 5.54 |
| 60 | 14.89 | 5.82 | 3.29 | 4.44 | 6.04 |
| 70 | 13.22 | 4.61 | 1.87 | 4.92 | 6.87 |
Fig. 9. Transport distances of mixed sands at different salinities. |
Fig. 10. Sedimentary facies maps of key sand groups of Upper Ganchaigou-Lower Youshashan formations superimposed on paleosalinity maps, southwestern Qaidam Basin. |
3.2. Debris input controls the scale and accumulation of beach-bar sand bodies
3.3. Ancient landform controls the shape and stacking style of beach-bar sandstone
Fig. 11. Ancient landforms and sections of beach-bar sand bodies of the Upper Ganchaigou Formation in southwestern Qaidam Basin. |
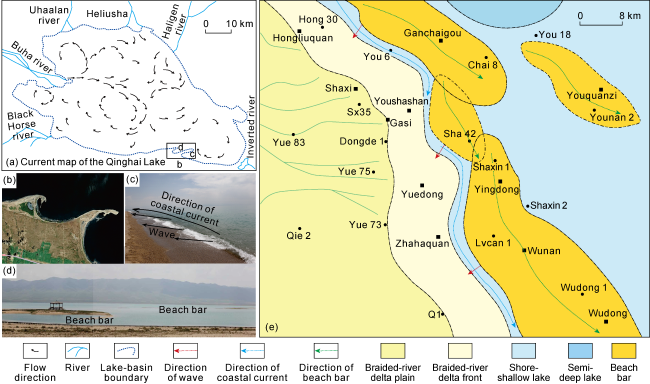
3.4. Monsoon driving effect controls the long axis extension direction of beach-bar sandstone
Fig. 12. Modern lake current and typical beach bars in the Qinghai Lake, and beach-bar sandstone map superimposed on wave and coastal current map in southwestern Qaidam Basin. |
4. Hydrocarbon accumulation of beach-bar sandstone in saline lake basin and its favorable exploration areas
4.1. Distribution of oil and gas in beach-bar sandstones and related reservoir types
4.1.1. Distribution of oil and gas in beach-bar sandstones
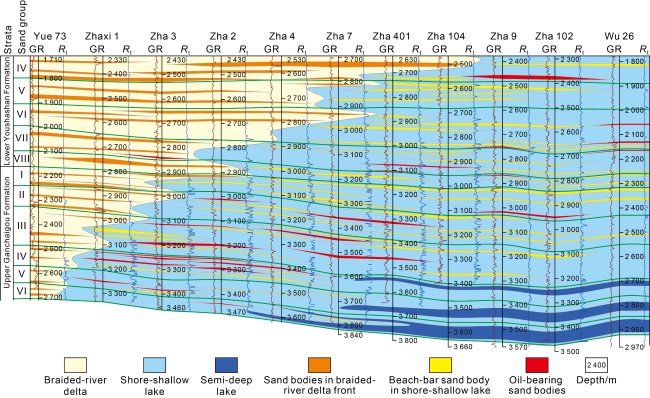
Fig. 13. The Upper Ganchaigou-Lower Youshashan stratigraphic section across wells Yue73 and Wu26 in southwestern Qaidam Basin (see |
4.1.2. Reservoir types and accumulation patterns
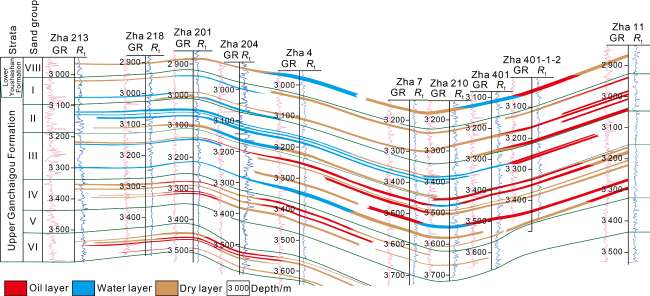
Fig. 14. The Upper Ganchaigou oil reservoir section across wells Zha213 and Zha11 in southwestern Qaidam Basin (see |
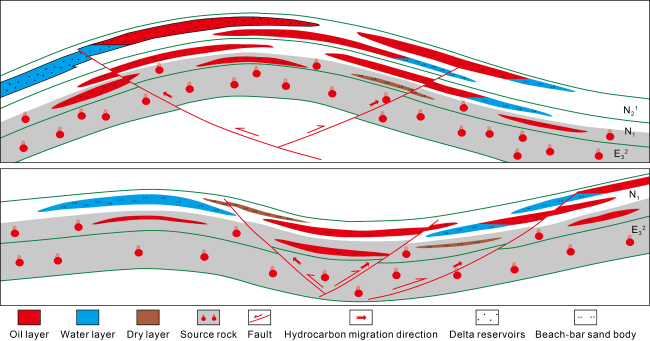
Fig. 15. Hydrocarbon accumulation patterns of beach-bar sand bodies in saline lake basin. |