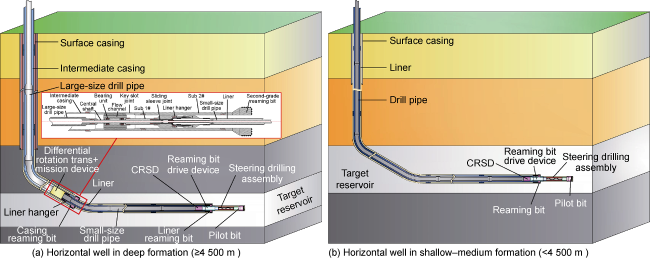
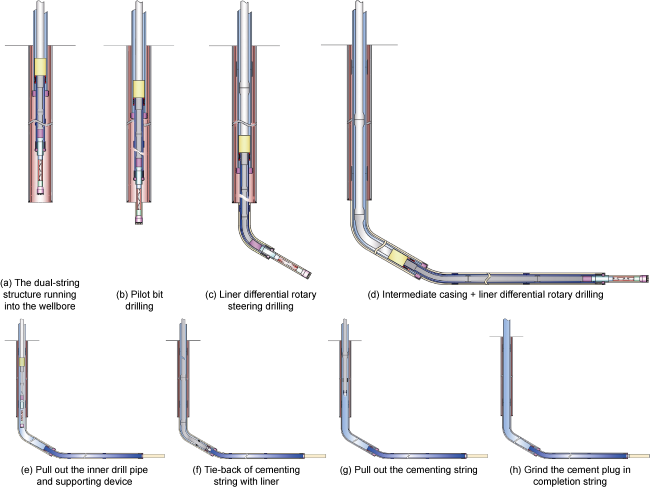
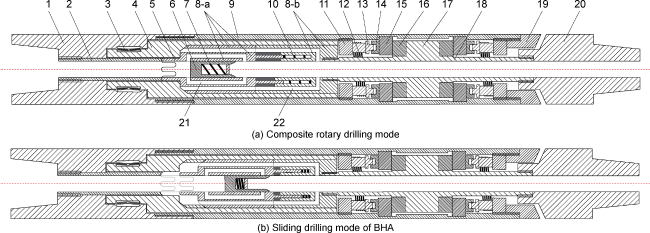
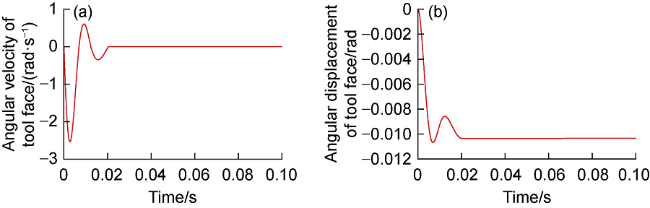
c—operating conditions such as pulling out of hole and running in hole;
d—dual-string structure, wellbore trajectory, downhole tools and other design parameters;
d2—inner diameter of the outer string, m;
D1—inner string diameter, m;
D2—outer string diameter, m;
E—elastic modulus of string, Pa;
F—axial tension of downhole string, N;
Ff—friction per unit length of the downhole string, N/m;
Fobj—objective function of extension limit of dual-string liner differential rotary drilling in horizontal well;
g—gravity acceleration, m/s2;
h—hydraulic constraints such as drilling fluid performance, hydraulic circulating pressure and critical flow velocity of rock debris migration;
i—well section element number;
I—moment of inertia of pipe cross-section, m4;
k—number of screen pipe elements;
kf—flow coefficient, dimensionless;
L—downhole string length, m;
Lh—hydraulic extension limit of dual-string liner drilling of horizontal well, m;
Li—length of well section i, m;
Lm—mechanical extension limit of dual-string liner drilling in horizontal well, m;
Lmax—maximum extension limit of dual-string liner drilling in horizontal well, m;
Lo—open hole extension limit of dual-string liner drilling in horizontal well, m;
MT1—inner string torque, N·m;
MT2—outer string torque, N·m;
n—rheology index, dimensionless;
nt1—normal force of the inner string acting on the outer string, N;
nt2—normal force of the dual-string acting on borehole wall, N;
N—element number of completion string, and $1\le i\le k\le N$;
pca—hydraulic loss in the annulus between downhole dual- string and borehole wall in the casing completion section, Pa;
pca1, pca2—hydraulic loss in annulus of casing-borehole wall and casing-drill pipe, Pa;
pf—reservoir fracture pressure, Pa;
pla—annulus pressure between the first-grade reaming bit at the front end of screen pipe and the borehole wall, Pa;
pla1, pla2—outer and inner annulus pressure, Pa;
pla1_b—outer annular circulation pressure of the well section with large deviation (greater than 30°), Pa;
pla1_h—outer annular circulation pressure of horizontal well section, Pa;
pla1_v—outer annular circulation pressure of the well section with small deviation (less than and equal to 30°), Pa;
pmax—the maximum hydraulic loss of downhole dual-string, Pa;
pmax,1—the maximum circulating hydraulic loss of downhole dual-string with the screen pipe and liner connected by screw thread, Pa;
pmax,2—the maximum circulating hydraulic loss of the downhole dual-string with the screen pipe hanging on the inner wall of the casing, Pa;
pp—hydraulic loss of downhole string, Pa;
P—mechanical parameters such as lifting system load, rotary system load and pipe failure limit;
∆p—pressure difference between outer annulus and inner annulus, Pa;
qw—gravity of downhole string per unit length in drilling fluid, N/m;
Qa—total drilling fluid flow rate in double-annulus, L/s;
Qa1—drilling fluid flow rate in outer annulus, L/s;
Qa2—drilling fluid flow rate in inner annulus, L/s;
Qc—critical drilling fluid displacement of wellbore cleaning, L/s;
va—drilling fluid flow velocity, m/s;
va1, va2—drilling fluid flow velocity in outer and inner annulus, m/s;
Y—allowable region of the constraint parameter, that is the constraint condition;
${{\kappa }_{\text{b}}}$—borehole curvature, m−1;
μ1—friction coefficient between inner string and outer string, dimensionless;
μ2—friction coefficient between borehole wall and outer string, dimensionless;
ρf—drilling fluid density, kg/m3.
kp—if kp=1, the inner and outer strings are small-size drill pipe and liner, respectively; if kp=2, the inner and outer strings are large-size drill pipe and intermediate casing, respectively.