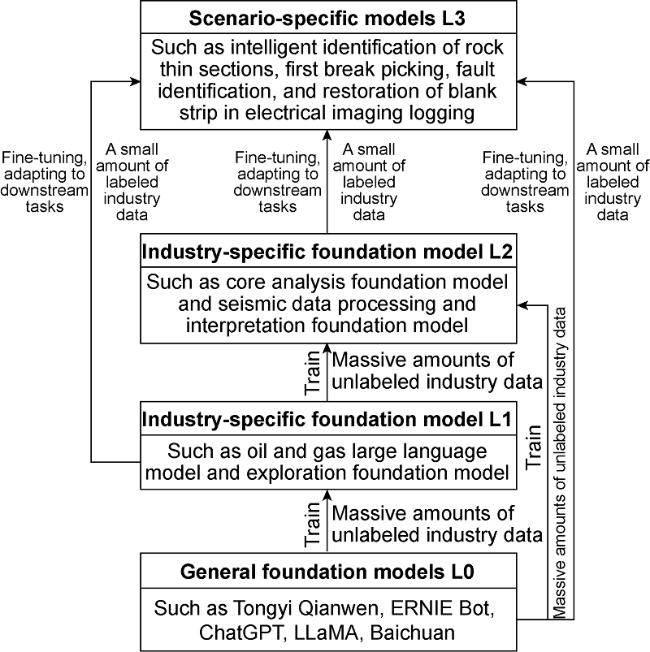
Within the legal domain, large language models that have been pre-trained on legal knowledge data are instrumental in automating the comprehension of legal cases and statutes, thereby providing professional, intelligent, and comprehensive legal information and services to both laypersons and legal practitioners. A collaborative effort by Zhejiang University, DAMO Academy, and UniDt has led to the development of the wisdomInterrogatory legal large model
[47], which builds upon the Baichuan-7B pre-trained model with secondary pre-training on legal knowledge data and instruction fine-tuning. This model is capable of generating legal documents and answering questions related to legal services. Alibaba Cloud’s Tongyi Farui
[48] offers legal intelligent dialogue systems that can autonomously synthesize legal claims from case descriptions and draft legal documents, in addition to facilitating legal knowledge search and legal text comprehension. LawGPT
[49], built on the ChatGLM-6B
[50] model, has been refined with a legal domain-specific dataset, which includes legal dialogues, question-and-answer datasets, and Chinese judicial examination questions, thereby enhancing the model’s basic semantic understanding in the legal domain and bolstering its capability to understand and enact legal content. Lawyer LLaMA
[51] has undergone extensive pre-training on a large legal corpus and is subsequently fine-tuned using data collected from legal professional qualification exams and legal consultations via ChatGPT, thereby equipping the model with practical application proficiency. DISC-LawLLM
[52] fine-tunes the Baichuan-13B model with the DISC-Law-SFT legal dataset and constructs the DISC-Law-Eval benchmark for evaluating legal language models. ChatLaw
[53] has been developed in various iterations to meet diverse legal service requirements, including ChatLaw-13B, ChatLaw-33B, and ChatLaw-Text2Vec. ChatLaw-13B is derived from fine-tuning the Ziya-LLaMA-13B-v1 model. ChatLaw-33B is trained on the Anima-33B model, further improving its logical reasoning abilities. ChatLaw-Text2Vec is a similarity-matching model fine-tuned on a dataset of judicial cases using BERT, designed to match users’ queries with relevant legal provisions. For the assembly of the training dataset, ChatLaw employs an extensive collection of raw textual materials, including legal news articles, legal forum discussions, legal provisions, judicial interpretations, legal consultations, judicial examination questions, and judicial decision texts, to fabricate a corpus of dialogic data.