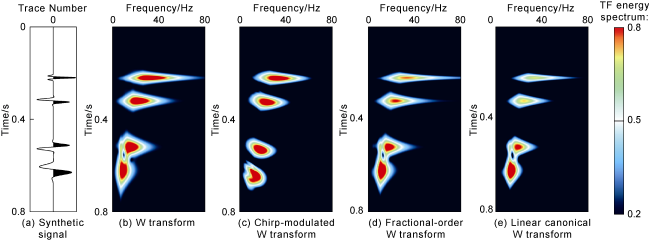
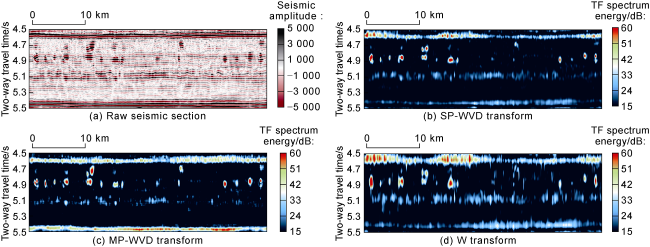
One of the most commonly used nonlinear time-frequency analysis methods for analyzing and processing seismic data is WVD
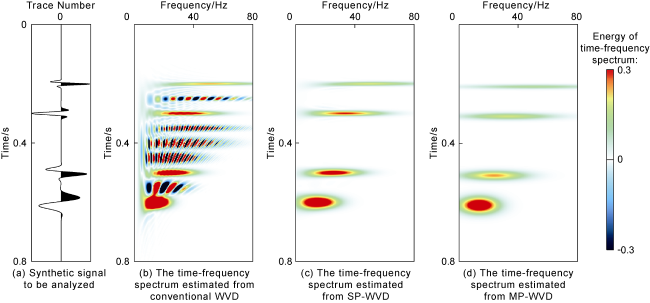
[6]. The WVD can be expressed as the instantaneous cross-correlation between the complex signal and its conjugate signal and provides high resolution and energy concentration in the time-frequency spectrum. However, the cross-correlation between different signal components leads to significant crosstalk in the time-frequency spectrum. Various enhancement methods are aimed at suppressing this crosstalk. For example, the smoothed pseudo-WVD (SP-WVD) proposed by Choi and Williams
[9] can effectively suppress crosstalk. The multi-channel WVD method with maximum entropy proposed by Wang et al. uses multiple WVD kernel functions to eliminate crosstalk between different components
[10]. Rao et al. proposed to use the multi-channel maximum entropy WVD to estimate the dominant frequency of seismic data for identifying karst cavities in strata to improve the accuracy of seismic anomaly identification
[11]. Alsalmi and Wang proposed the masked WVD method, in which a stable mask filter is constructed for post-processing the results of WVD time-frequency analysis
[12]. These improved methods can all be regarded as filtering the time-frequency spectrum, which inevitably removes part of the valuable energy.