Introduction
1. Regional geological setting
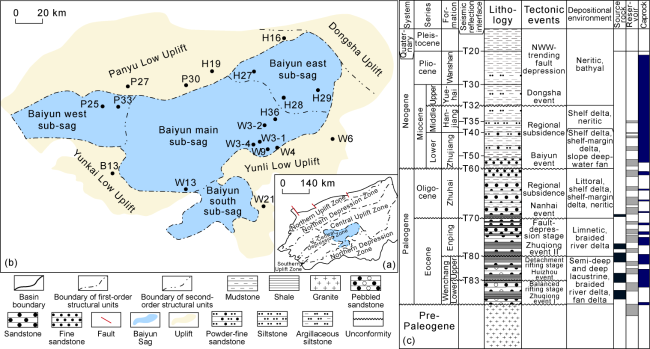
Fig. 1. Structural division of the Pearl River Mouth Basin (a), structural division of the Baiyun Sag (b) and comprehensive stratigraphic column of the Baiyun Sag (c). |
2. Geochemical characteristics of source rocks and oil and gas source correlation
2.1. Geochemical characteristics of source rocks
Table 1. Organic geochemical parameters of different source rocks in the Wenchang Formation and Enping Formation in the Baiyun Sag |
| Well | Formation | Sedimentary facies | Pr/Ph | Terrestrial higher plants | Algae | Sporopollen and algae | Carbon isotopes of kerogen/‰ | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OL/C30 H | T/C30 H | C304-methyl steranes | Triaromatic dinosteranes | Sporopollen/% | Algae/ % | |||||
| W3-2, W4 | Wenchang | Semi-deep lacustrine | 1.1-1.9 | 0.2-0.3 | 0.3-1.2 | rare-rich | none | 9-80 | 20-91 | −29.2 to −28.5 |
| W3-4, H36 | Wenchang | Shallow lacustrine | 2.3-2.6 | 0.4-1.6 | 3.5-6.9 | none | none | 70-99 | 1-30 | −27.3 to −27.1 |
| H27 | Enping | Shallow lacustrine | 2.8-4.5 | 0.5-0.7 | 1.1-4.4 | none | none | 92-99 | 1-8 | −27.7 to −27.0 |
| P33, P25 | Enping | Delta | 3.2-4.8 | 0.1-0.3 | 5.3-5.9 | none | none | 94-99 | 1-6 | −27.3 to −27.0 |
| H29, H36 | Enping | Marine-continental transitional | 1.3-1.7 | 0.8-2.9 | 0.7-7.5 | none | rich | 47-53 | 47-53 | −26.2 to −24.9 |
Note: Pr represents pristane; Ph represents phytane; OL represents oleanane; C30 H means C30 17α(H), 21β(H)-hopane; T means bicadinane-T. |
2.2. Oil and gas source correlation
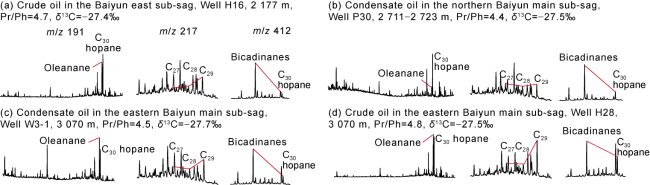
Fig. 2. Biomarkers of Zhujiang Formation crude oils in different zones of the Baiyun Sag. |
3. Tectonic-thermal evolution
3.1. Distribution of present geothermal field
3.2. Tectonic-thermal evolution history
4. Simulation of thermal evolution history and hydrocarbon generation history of source rocks
4.1. Simulation of thermal evolution history of source rocks based on basin modeling technology
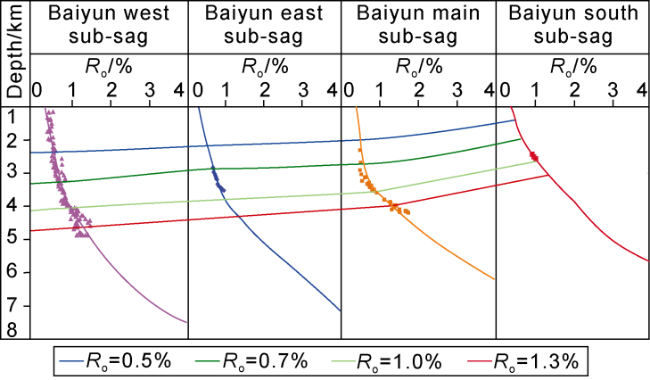
Fig. 3. Ro values evolution with burial depth of source rocks in different sub-sags of the Baiyun Sag. |
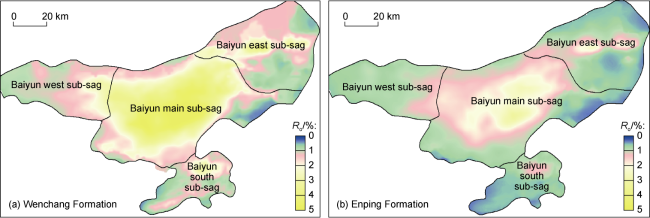
Fig. 4. Prediction of current Ro of source rocks in the Baiyun Sag |
4.2. Reconstruction of hydrocarbon generation history of source rocks
Table 2. Geochemical parameters of mudstone samples from the Baiyun Sag and the Zhu I Depression |
| Well | Depth/ m | Structural location | Formation | Sedimentary facies | Lithology | Pr/Ph | Ro/ % | TOC/ % | HI/ (mg·g−1) | Ratio of kerogen element content | Carbon isotope composition of kerogen/‰ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H/C | O/C | |||||||||||
| P5 | 3 488- 3 500 | Panyu 4 sub-sag, Zhu I Depression | Wenchang Formation | Semi-deep lacustrine | Mudstone | 2.1 | 0.70 | 5.2 | 534 | 1.47 | 0.08 | −26.3 |
| W3-2 | 4 880- 4 930 | Baiyun main sub-sag | Wenchang Formation | Semi-deep lacustrine | Mudstone | 1.1 | 1.10 | 1.0 | 272 | 1.16 | 0.11 | −28.0 |
| W3-4 | 4 295- 4 335 | Baiyun main sub-sag | Wenchang Formation | Shallow lacustrine | Mudstone | 2.6 | 0.80 | 1.3 | 236 | 1.03 | 0.13 | −28.0 |
| H27 | 4 655- 4 690 | Baiyun east sub-sag | Enping Formation | Shallow lacustrine | Mudstone | 3.6 | 0.99 | 2.7 | 150 | 0.60 | 0.10 | −27.7 |
| P33 | 4 455- 4 480 | Baiyun west sub-sag | Enping Formation | Delta | Mudstone | 5.2 | 1.07 | 1.6 | 144 | 0.46 | 0.06 | −27.0 |
| W3-1 | 3 508- 3 509 | Baiyun east sub-sag | Zhuhai Formation | Marine | Mudstone | 2.4 | 0.60 | 0.9 | 188 | 1.04 | 0.11 | −24.9 |
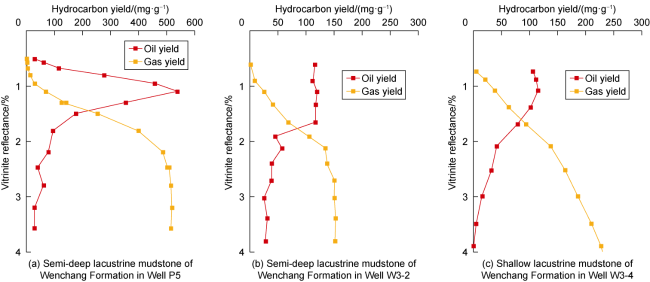
Fig. 5. Simulation of hydrocarbon generation of different types of source rocks in the Baiyun Sag. |
5. Prediction of oil and gas resource distribution
5.1. Oil and gas resource evaluation
5.2. Simulation and evaluation of hydrocarbon migration and accumulation units
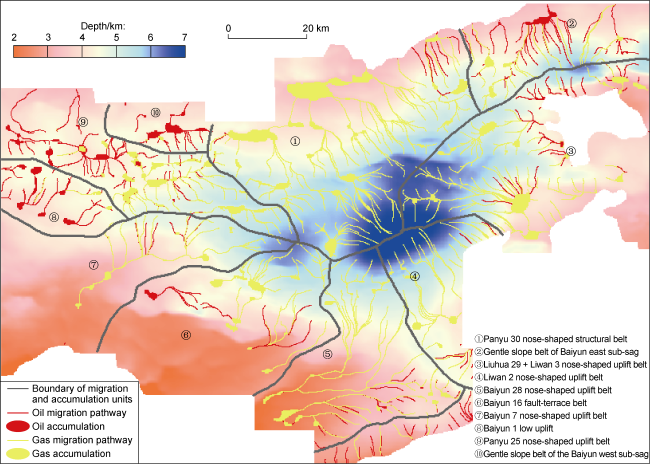
Fig. 6. Overlapping diagram of migration and accumulation unit division and hydrocarbon migration flow potential on Enping Formation top of the Baiyun Sag. |
Table 3. Comprehensive evaluation of each migration and accumulation unit in the Baiyun Sag |
| Unit No. | Favorable zone of migration and accumulation | Type of hydrocarbon supply flow | Convergent area/km2 | Accumulation amount/108 t | Accumulation abundance/ (104 t∙km−2) | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ① | Panyu 30 nose-shaped structural belt | Convergent flow | 2 114 | 5.340 0 | 25.26 | I |
| ② | Gentle slope belt of Baiyun east sub-sag | Convergent flow | 808 | 1.510 0 | 18.69 | II |
| ③ | Liuhua 29 + Liwan 3 nose-shaped uplift belt | Convergent flow | 1 948 | 4.910 0 | 25.21 | I |
| ④ | Liwan 2 nose-shaped uplift belt | Parallel flow | 962 | 0.432 0 | 4.49 | III |
| ⑤ | Baiyun 28 nose-shaped uplift belt | Convergent flow | 2 371 | 1.120 0 | 4.72 | III |
| ⑥ | Baiyun 16 fault-terrace belt | Parallel flow | 750 | 0.571 0 | 7.61 | III |
| ⑦ | Baiyun 7 nose-shaped uplift belt | Convergent flow | 682 | 0.335 1 | 4.91 | III |
| ⑧ | Baiyun 1 low uplift | Parallel flow | 765 | 0.927 2 | 12.12 | II |
| ⑨ | Panyu 25 nose-shaped uplift belt | Convergent flow | 1 246 | 0.536 4 | 4.30 | III |
| ⑩ | Gentle slope belt of the Baiyun west sub-sag | Parallel flow | 409 | 0.113 9 | 2.79 | III |